# 硬件在环仿真(HITL)
硬件在环仿真模式 (HITL 或 HIL) 下 PX4 固件代码运行在真实的飞行控制器硬件平台上。 这种方法的优点是可以在实际硬件上测试大多数的实际飞行代码。
HITL 模式下 PX4 支持多旋翼 (使用 jMAVSim 或者 Gazebo) 和固定翼 (使用 Gazebo 或者 X-Plane demo/full version) 无人机的仿真。
# HITL兼容机架
目前兼容的机架构型和模拟器的情况如下:
| 机架 | SYS_AUTOSTART | Gazebo | jMAVSim |
|---|---|---|---|
| HIL Quadcopter X | 1001 | Y | |
| HIL Standard VTOL QuadPlane | 1002 | Y | Y |
| HIL Standard VTOL QuadPlane | 4001 | Y | |
| Generic Quadrotor x copter | 4011 | Y | Y |
| DJI Flame Wheel f450 | 4011 | Y | Y |
# HITL 仿真环境
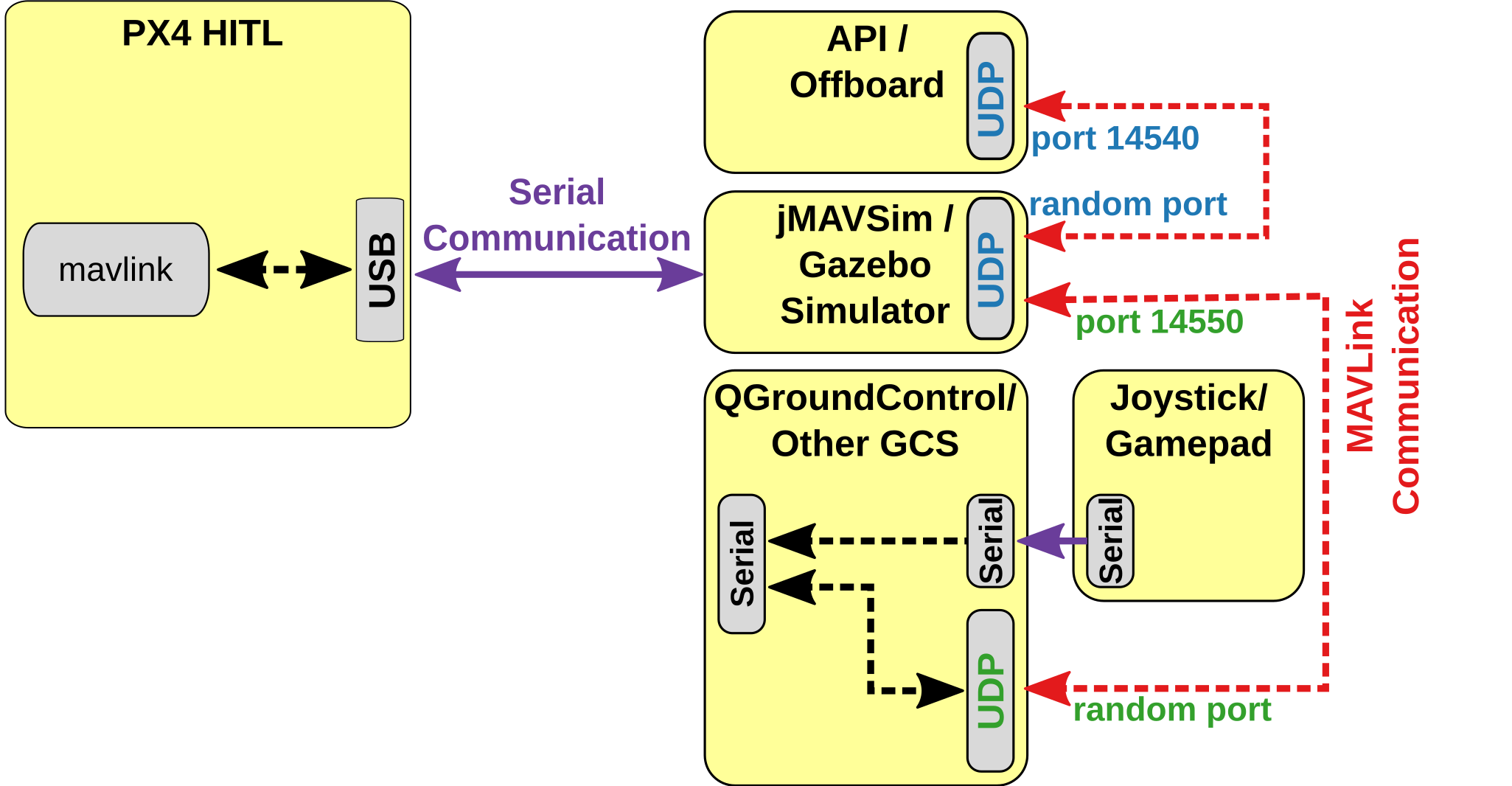
硬件在环仿真(HITL)模式下标准的 PX4 固件在真实的硬件上运行。 JMAVSim 或 Gazebo (运行在开发计算机上) 通过 USB/UART 完成与飞行控制器硬件平台的连接。 模拟器充当在 PX4 和 QGroundControl 之间共享 MAVLink 数据的网关。
注解
The simulator can also be connected via UDP if the flight controller has networking support and uses a stable, low-latency connection (e.g. a wired Ethernet connection - WiFi is usually not sufficiently reliable). For example, this configuration has been tested with PX4 running on a Raspberry Pi connected via Ethernet to the computer (a startup configuration that includes the command for running jMAVSim can be found here (opens new window)).
The diagram below shows the simulation environment:
- 飞控板 HITL 模式被激活 (通过 QGroundControl) ,该模式下不会启动飞控板上任何传感器。
- jMAVSim 或者 Gazebo 通过 USB 连接到飞控板。
- 模拟器通过 UDP 连接到 QGroundControl 并将 MAVLink 数据传输至 PX4 。
- (可选) 通过串口可将操纵杆/游戏手柄通过 QGroundControl 连接至仿真回路中。
- (可选 - 仅适用于Gazebo) Gazebo 还可以连接到一个 offboard API ,并将 MAVLink 数据桥接到 PX4 。
# HITL 相比于 SITL
相比之下, HITL 在正常飞控硬件平台上运行正常的处于 ”HITL 模式“ 的 PX4 固件。 仿真数据进入整个仿真系统的时间点与 SITL 有所不同。
By contrast, HITL runs normal PX4 firmware in "HITL mode", on normal hardware. The simulation data enters the system at a different point than for SITL. Core modules like commander and sensors have HITL modes at startup that bypass some of the normal functionality.
完成所有的配置设定后 关闭 QGroundControl 并断开飞控板与计算机的连接。
# 配置 HITL
# JMAVSim/Gazebo HITL 仿真环境
- 通过 USB 将自动驾驶仪直接连接到 QGroundControl。
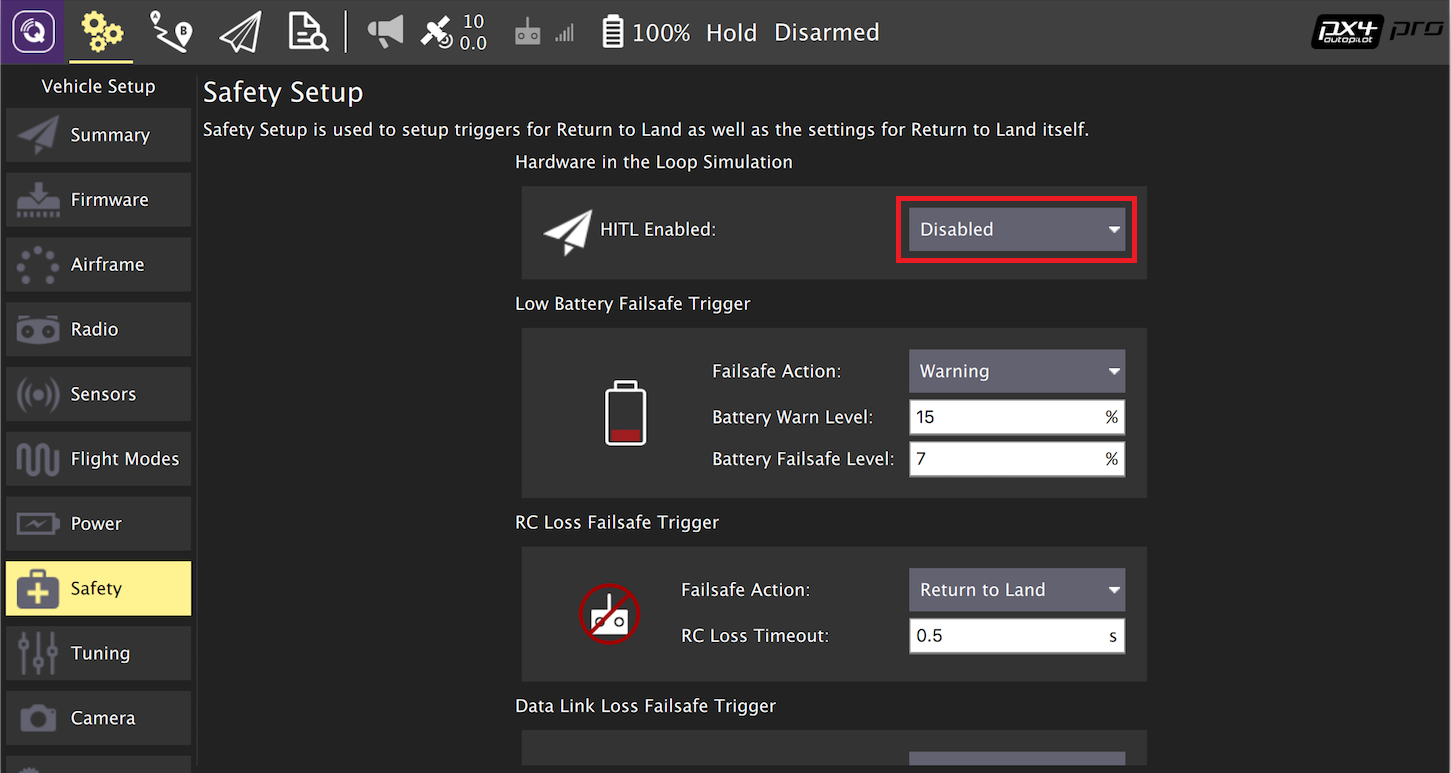
- 激活 HITL 模式
打开 Setup > Safety 选项卡。
在 HITL Enabled 下拉框中选择 Enabled 完成 HITL 模式的激活。
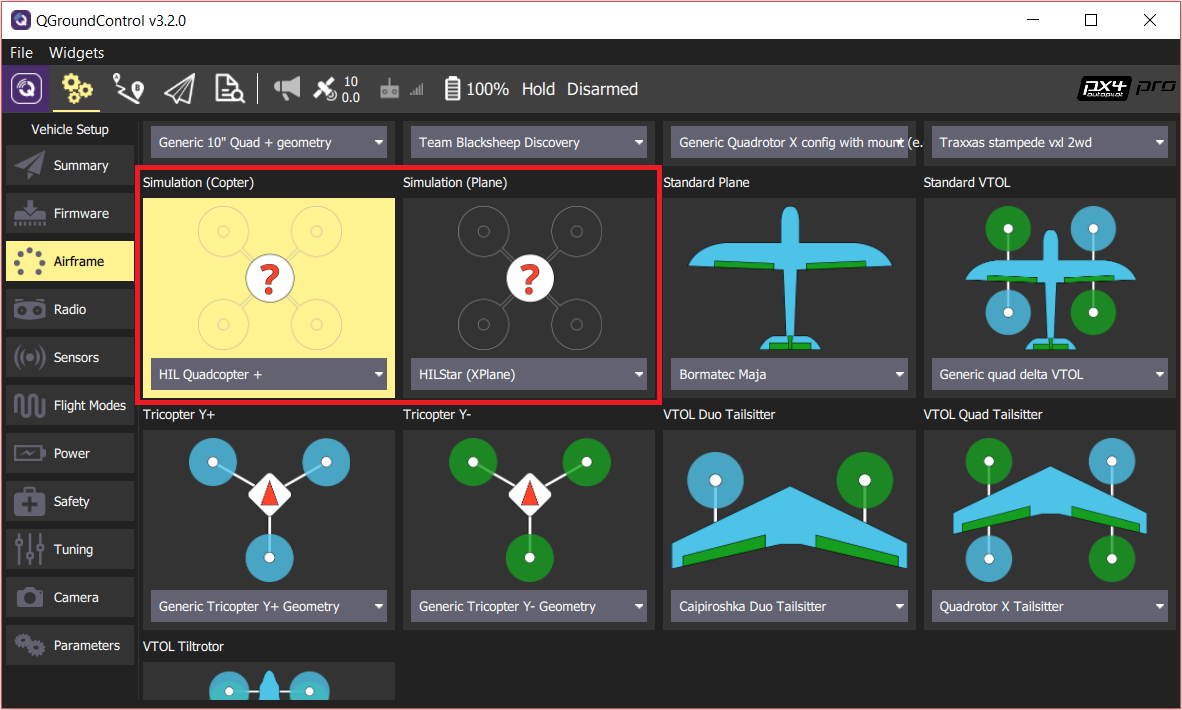
- 选择机架
打开 Setup > Airframes 选项卡。
选择一个你想要进行测试的 兼容的机架 。 Then click Apply and Restart on top-right of the Airframe Setup page.
- 如有必要, 校准您的 RC 遥控器 或操纵杆。
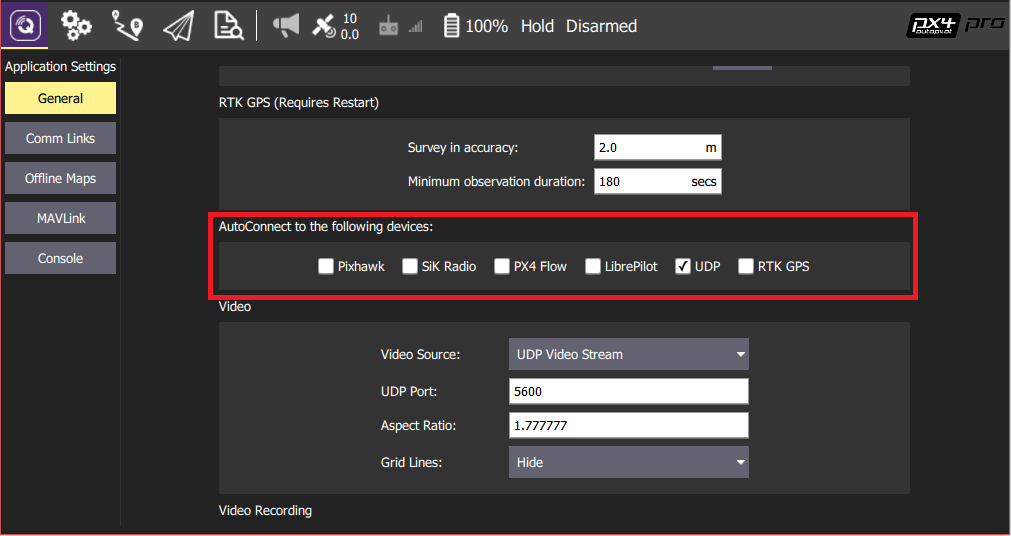
- 设置 UDP
在设置菜单的 "General" 选项卡下, 取消选中 AutoConnect 一栏中除 UDP 外的所有复选框。
- (可选) 配置操纵杆和故障保护。 设置以下 parameters (opens new window) 以便使用操纵杆而不是 RC 遥控器:
- COM_RC_IN_MODE 更改为 "Joystick/No RC Checks". 这允许操纵杆输入并禁用 RC 输入检查。 这允许操纵杆输入并禁用 RC 输入检查。
- NAV_DLL_ACT 更改为 "Disabled"。 这可确保在没有无线遥控的情况下运行 HITL 时 RC 失控保护不会介入。
提示
The QGroundControl User Guide also has instructions on Joystick (opens new window) and Virtual Joystick (opens new window) setup.
遵循以下流程进行 X-Plane 模拟器的配置:
# X-Plane HITL 仿真环境
总而言之, HITL 在真实硬件上运行标准 PX4 固件,而 SITL 实际上要比标准 PX4 系统执行更多的代码。
# Gazebo
注解
Make sure QGroundControl is not running!
- 更新环境变量:
cd <Firmware_clone> make px4_sitl_default gazebo - 打开载具模型的 sdf 文件(例如 Tools/sitl_gazebo/models/iris/iris.sdf)。
- 找到文件的
mavlink_interface plugin分区,将serialEnabled和hil_mode参数更改为true。
注解
The serial device depends on what port is used to connect the vehicle to the computer (this is usually /dev/ttyACM0). An easy way to check on Ubuntu is to plug in the autopilot, open up a terminal, and type dmesg | grep "tty". The correct device will be the last one shown.
- Set up the environment variables:and run Gazebo in HITL mode:
source Tools/setup_gazebo.bash $(pwd) $(pwd)/build/px4_sitl_defaultgazebo Tools/sitl_gazebo/worlds/hitl_iris.world - Start QGroundControl. It should autoconnect to PX4 and Gazebo.
# jMAVSim (仅适用于四旋翼无人机)
注解
Make sure QGroundControl is not running!
- 将飞行控制器连接到计算机, 并等待其启动。
- 在 HITL 模式下运行 jMAVSim (r如有必要,修改串口号名称
/dev/ttyACM0- 比如,在 Mac OS 上该参数应为/dev/tty.usbmodem1): sh ./Tools/jmavsim_run.sh -q -d /dev/ttyACM0 -b 921600 -r 250./Tools/jmavsim_run.sh -q -s -d /dev/ttyACM0 -b 921600 -r 250
注解
Replace the serial port name /dev/ttyACM0 as appropriate. On macOS this port would be /dev/tty.usbmodem1. On Windows (including Cygwin) it would be the COM1 or another port - check the connection in the Windows Device Manager.
- 开启 QGroundControl。 它应该会自动连接 PX4 和 Gazebo 。
# 在 HITL 仿真中执行自主飞行任务
You should be able to use QGroundControl to run missions (opens new window) and otherwise control the vehicle.