# ARK RTK GPS
ARK RTK GPS is an open source UAVCAN RTK GPS, u-blox F9P (opens new window), magnetometer, barometer, IMU, buzzer, and safety switch module.

# Where to Buy
Order this module from:
# Specifications
- Open Source Schematic and BOM (opens new window)
- Runs PX4 Open Source Firmware (opens new window)
- Supports UAVCAN Firmware Updating
- Dynamic UAVCAN node enumeration
- Sensors
- Ublox F9P GPS
- Multi-band GNSS receiver delivers centimeter level accuracy in seconds
- Concurrent reception of GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and BeiDou
- Multi-band RTK with fast convergence times and reliable performance
- High update rate for highly dynamic applications
- Centimeter accuracy in a small and energy efficient module
- Bosch BMM150 Magnetometer
- Bosch BMP388 Barometer
- Invensense ICM-42688-P 6-Axis IMU
- Ublox F9P GPS
- STM32F412CEU6 MCU
- Safety Button
- Buzzer
- Two Pixhawk Standard CAN Connectors
- 4 Pin JST GH
- F9P “UART 2” Connector
- 3 Pin JST GH
- TX, RX, GND
- Pixhawk Standard Debug Connector
- 6 Pin JST SH
- LED Indicators
- Safety LED
- GPS Fix
- RTK Status
- RGB system status
- USA Built
- Power Requirements
- 5V
- 170mA Average
- 180mA Max
# Wiring/Connecting
The ARK RTK GPS is connected to the CAN bus using a Pixhawk standard 4 pin JST GH cable. Multiple sensors can be connected by plugging additional sensors into the ARK RTK GPS's second CAN connector.
General instructions for UAVCAN wiring can also be found in UAVCAN > Wiring.
# Mounting/Orientation
The ARK RTK GPS must be mounted with the connectors on the board pointing towards the back of vehicle, as shown in the following picture.
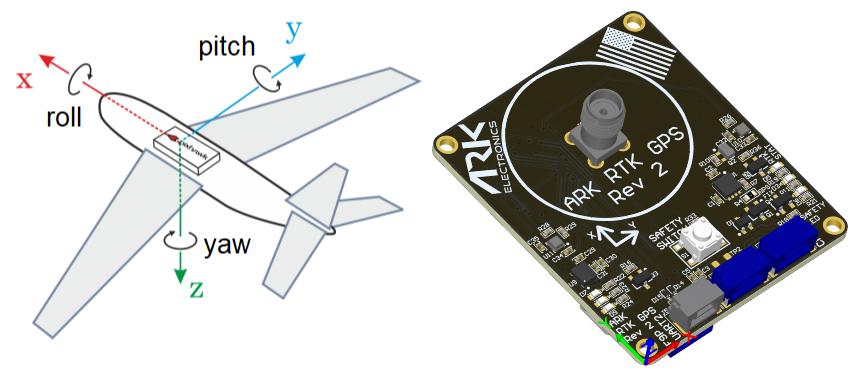
The sensor can be mounted anywhere on the frame, but you will need to specify its position, relative to vehicle centre of gravity, during PX4 configuration.
# PX4 Setup
# Enabling UAVCAN
In order to use the ARK RTK GPS, connect it to the Pixhawk CAN bus and enable the UAVCAN driver by setting parameter UAVCAN_ENABLE to 2 for dynamic node allocation (or 3 if using UAVCAN ESCs).
The steps are:
- In QGroundControl set the parameter UAVCAN_ENABLE to
2or3and reboot (see Finding/Updating Parameters). - Connect ARK RTK GPS CAN to the Pixhawk CAN.
Once enabled, the module will be detected on boot. GPS data should arrive at 10Hz.
General instructions for UAVCAN PX4 configuration can also be found in UAVCAN > PX4 Configuration.
# PX4 Configuration
You need to set necessary UAVCAN parameters and define offsets if the sensor is not centred within the vehicle.
- Enable GPS yaw fusion by setting bit 7 of EKF2_AID_MASK to true.
- Enable GPS blending to ensure the heading is always published by setting SENS_GPS_MASK to 7 (all three bits checked).
- Enable UAVCAN_SUB_GPS, UAVCAN_SUB_MAG, and UAVCAN_SUB_BARO.
- Set CANNODE_TERM to
1if this is that last node on the CAN bus. - The parameters EKF2_GPS_POS_X, EKF2_GPS_POS_Y and EKF2_GPS_POS_Z can be set to account for the offset of the ARK RTK GPS from the vehicles centre of gravity.
# Setting Up Moving Baseline & GPS Heading
The simplest way to set up moving baseline and GPS heading with two ARK RTK GPS modules is via CAN, though it can be done via UART to reduce traffic on the CAN bus if desired.
Setup via CAN:
- Ensure the ARK RTK GPS modules are connected to the Pixhawk via CAN (one can connect to another's secondary CAN port).
- Choose one ARK RTK GPS to be the Rover and one to be the Moving Base.
- Reopen QGroundControl, go to parameters, and select
Standardto hide that dropdown and selectComponent ##to view each of your ARK RTK GPS's CAN node parameters :::noteComponent ##won't be visible unless the ARK RTK GPS is connected to the Pixhawk prior to opening QGroundControl. ::: - On the Rover, set the following:
- GPS_UBX_MODE to
3 - GPS_YAW_OFFSET to
0if your Rover is in front of your Moving Base,90if Rover is right of Moving Base,180if Rover is behind Moving Base, or270if Rover is left of Moving Base.
- GPS_UBX_MODE to
- On the Moving Base, set the following:
- GPS_UBX_MODE to
4.
- GPS_UBX_MODE to
Setup via UART:
- Ensure the ARK RTK GPS modules are connected to the Pixhawk via CAN.
- Ensure the ARK RTK GPS modules are connected to each other via their UART2 port (UART2 pinout shown below). Note that TX of one module needs to connect with RX of the other.
| Pin | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | TX |
| 2 | RX |
| 3 | GND |
- Setup at this point is the same as via CAN, detailed above, except that GPS_UBX_MODE is set to
1on the Rover and2on the Moving Base.
# Building ARK RTK GPS Firmware
ARK RTK GPS is sold with a recent firmware build. Developers who want to update to the very latest version can build and install it themselves using the normal PX4 toolchain and sources.
The steps are:
- Install the PX4 toolchain.
- Clone the PX4-Autopilot sources, including ARK RTK GPS, using git:
git clone https://github.com/PX4/PX4-Autopilot --recursive cd PX4-Autopilot - Build the ARK RTK GPS firmware:
make ark_can-rtk-gps_default - That will have created a binary in build/ark_can-rtk-gps_default named XX-X.X.XXXXXXXX.uavcan.bin. Put this binary on the root directory of the flight controller’s SD card to flash the ARK RTK GPS. Next time you power your flight controller with the SD card installed, ARK RTK GPS will automatically be flashed and you should notice the binary is no longer in the root directory and there is now a file named 80.bin in the ufw directory of the SD card.
注解
ARK RTK GPS will not boot if there is no SD card in the flight controller when powered on.
# Updating ARK RTK GPS Bootloader
ARK RTK GPS comes with the bootloader pre-installed. You can rebuild and reflash it within the PX4-Autopilot environment if desired.
The steps are:
- Build the ARK RTK GPS bootloader firmware:
make ark_can-rtk-gps_canbootloader
注解
This will setup your launch.json file if you are in VS code. If using the Black Magic Probe and VS code, make sure to update BMPGDBSerialPort within this file to the correct port that your debugger is connected to. On MacOS, the port name should look something like cu.usbmodemE4CCA0E11.
- Connect your ARK RTK GPS to any Serial Wire Debugging (SWD) device that supports use of GNU Project Debugger (GDB), such as the Black Magic Probe, and then connect power to your ARK RTK GPS via one of the CAN ports.
- Flash the ARK RTK GPS with
ark_can-rtk-gps_canbootloader. To do so in VS code, you should seeCMake: [ark_can-rtk-gps_canbootloader]: Readyon the bottom bar of VS code, indicating what you are flashing. You then flash the bootloader by selectingStart Debuggingin the Run and Debug window of VS code. - With the bootloader flashed, you are ready to build and flash the ARK RTK GPS firmware
ark_can-rtk-gps_defaultas outlined above.
# Updating Ublox F9P Module
ARK RTK GPS comes with the Ublox F9P module up to date with version 1.13 or newer. However, you can check the version and update the firmware if desired.
The steps are:
- Download u-center from u-blox.com (opens new window) and install on your PC (Windows only)
- Open the u-blox ZED-F9P website (opens new window)
- Scroll down and click on the "Show Legacy Documents" box
- Scroll down again to Firmware Update and download your desired firmware (at least version 1.13 is needed)
- While holding down the safety switch on the ARK RTK GPS, connect it to power via one of its CAN ports and hold until all 3 LEDs blink rapidly
- Connect the ARK RTK GPS to your PC via its debug port with a cable such as the Black Magic Probe or an FTDI
- Open u-center, select the COM port for the ARK RTK GPS and connect
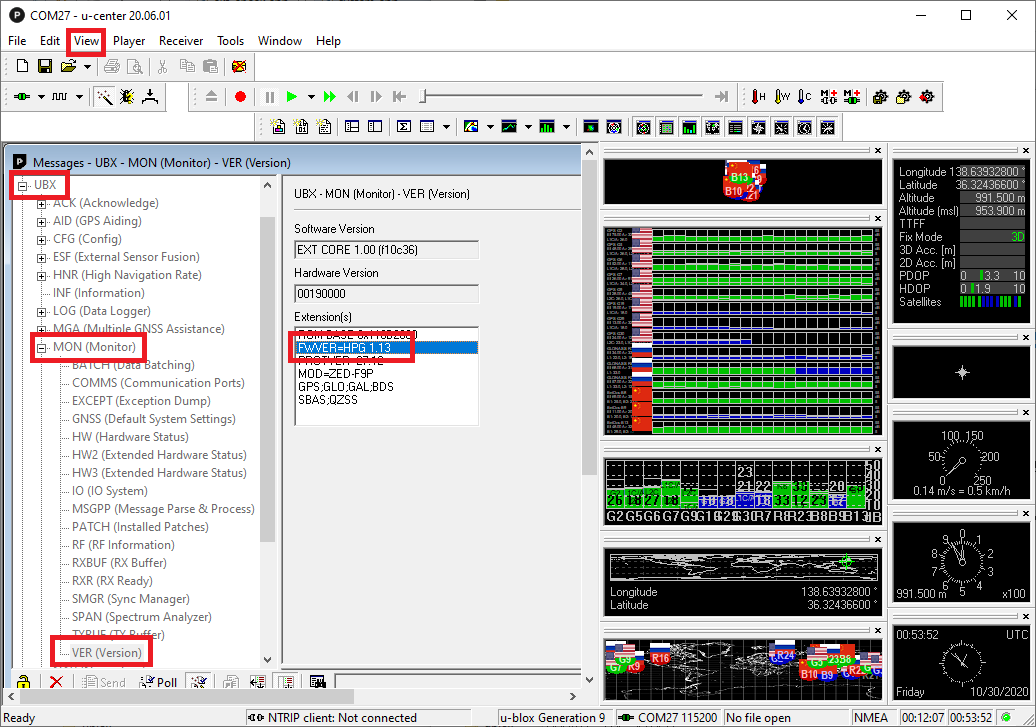
- Check the current firmware version by selecting View, Messages View, UBX, MON, VER
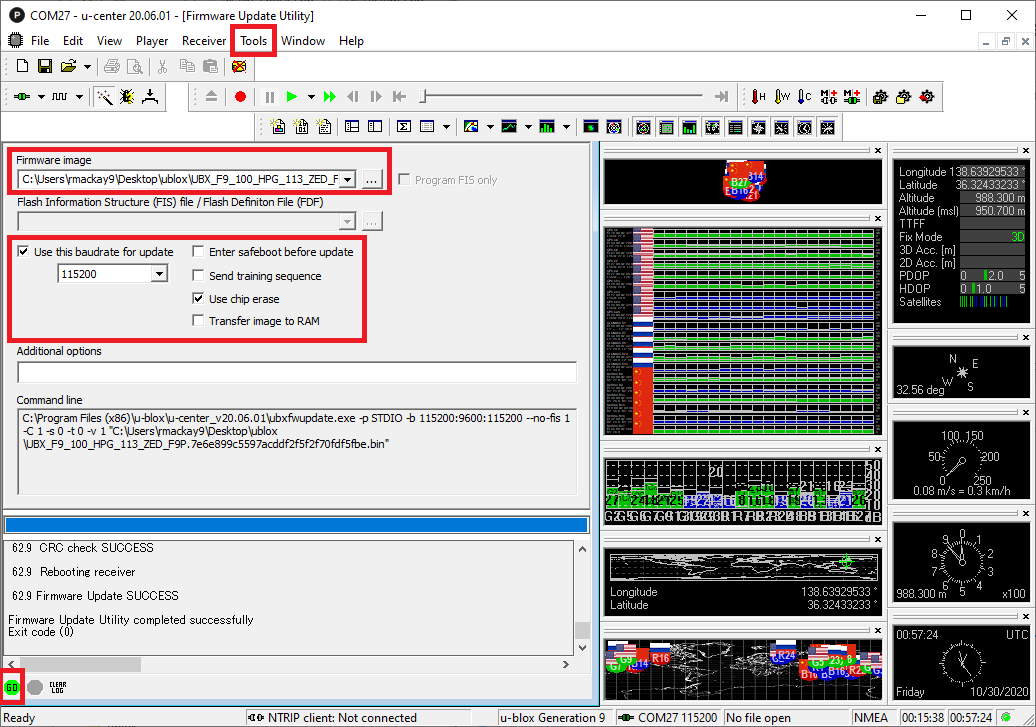
- To update the firmware:
- Select Tools, Firmware Update
- The Firmware image field should be the .bin file downloaded from the u-blox ZED-F9P website
- Check the "Use this baudrate for update" checkbox and select 115200 from the drop-down
- Ensure the other checkboxes are as shown below
- Push the green GO button on the bottom left
- "Firmware Update SUCCESS" should be displayed if it updated successfully
# LED Meanings
You will see green, blue and red LEDs on the ARK RTK GPS when it is being flashed, a blinking green LED if it is running properly, and a blinking or solid blue LED on the Rover ARK RTK GPS when it is receiving RTCM corrections.
If you see a red LED there is an error and you should check the following:
- Make sure the flight controller has an SD card installed.
- Make sure the ARK RTK GPS has
ark_can-rtk-gps_canbootloaderinstalled prior to flashingark_can-rtk-gps_default. - Remove binaries from the root and ufw directories of the SD card and try to build and flash again.