# 基本概念
本主题提供了无人机和使用 PX4 的基本介绍(主要面向新手用户,但对有经验的用户也是一个很好的介绍)。
如果你已经熟悉了基本概念,你可以转到 基本组装 以了解如何连接特定的自驾仪硬件。 To load firmware and set up the vehicle with QGroundControl, see Basic Configuration.
# 无人机是什么?
无人机是无人驾驶的“机器人”设备,可以远程或自动控制。
无人机可被用于 消费级、工业级、政府、军工应用 (opens new window)。 这包括(非详尽):航空摄影/录像,载货,竞速,搜索和测绘等。
Different types of drones are used for air, ground, sea, and underwater. 这些(更正式地)被称为无人驾驶飞行器(UAV),无人驾驶飞行器系统(UAS),无人驾驶地面车辆(UGV),无人驾驶水面船只(USV),无人驾驶水下潜航器(UUV)。
无人机的“大脑”被称为自动驾驶仪。 It consists of flight stack software running on vehicle controller ("flight controller") hardware.
Some drones also have a separate on-vehicle companion computer. These provide powerful general-purpose computing platform for networking, computer vision, and many other tasks.
# PX4 自动驾驶仪
PX4 (opens new window) is powerful open source autopilot flight stack.
PX4的一些主要功能包括:
- Controls many different vehicle frames/types, including: aircraft (multicopters, fixed-wing aircraft and VTOLs), ground vehicles and underwater vehicles.
- 适用于设备控制器,传感器和其他外围设备的硬件选择。
- 灵活而强大的飞行模式和安全功能。
- Robust and deep integration with companion computers and robotics APIs (ROS 2, MAVSDK (opens new window)).
PX4是一个大型无人机平台的核心部分,整个平台包括了QGroundControl地面站,Pixhawk硬件设备 (opens new window),以及MAVSDK (opens new window)用于集成记载计算机,相机和其他使用MAVLink协议的硬件设备。 PX4 由 Dronecode 项目 (opens new window) 支持。
# QGroundControl
Dronecode 地面控制站称为 QGC 地面站 (opens new window)。 You can use QGroundControl to load (flash) PX4 onto the vehicle control hardware, you can setup the vehicle, change different parameters, get real-time flight information and create and execute fully autonomous missions.
QGroundControl runs on Windows, Android, MacOS or Linux. 从这里 (opens new window)下载并安装。
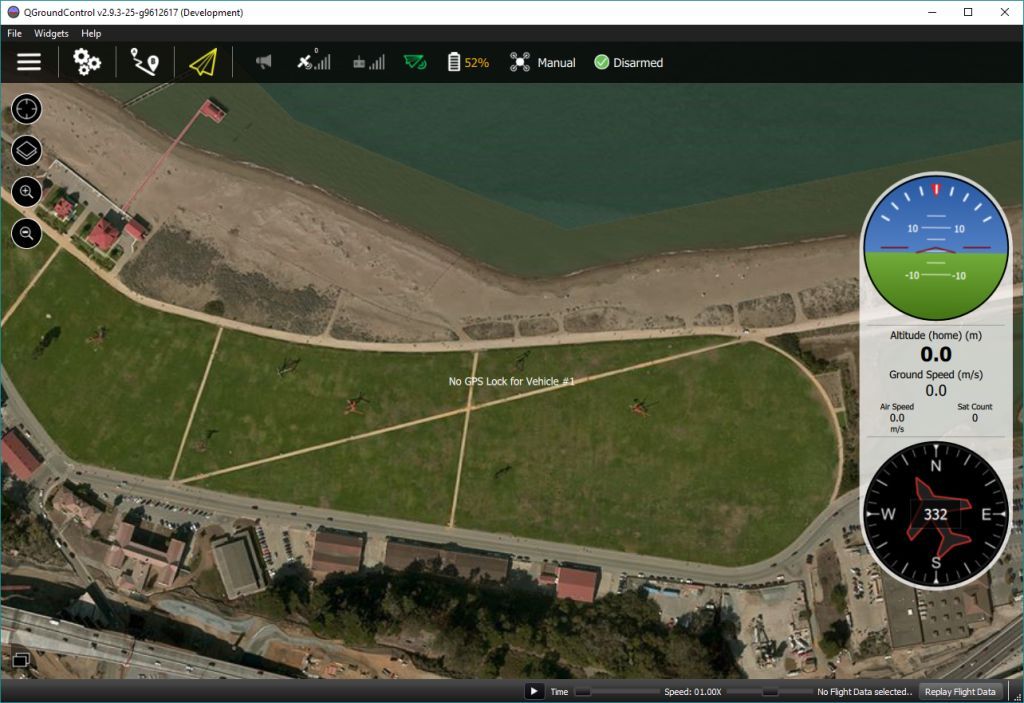
# 机体/飞行控制板
PX4最初设计用于在Pixhawk系列飞控上运行,但是现在可以在Linux计算机或者其他硬件上运行。 在选择飞控板时你应当考虑飞机的物理尺寸限制、想要进行的活动,当然还需要考虑成本。
更多信息,请参阅飞行控制器选择。
# 传感器
PX4使用传感器确定机体状态(这是稳定和启动自动控制所必须的)。 The system minimally requires a gyroscope, accelerometer, magnetometer (compass) and barometer. GPS和其他定位系统是启用所有的自动模式以及部分辅助模式所必须的。 Fixed-wing and VTOL-vehicles should additionally include an airspeed sensor (very highly recommended).
更多信息请参阅:
# 输出:电机,舵机,执行器
PX4 uses outputs to control: motor speed (e.g. via ESC), flight surfaces like ailerons and flaps, camera triggers, parachutes, grippers, and many other types of payloads.
The outputs may be PWM ports or DroneCAN nodes (e.g. DroneCAN motor controllers). 下面的图片显示了Pixhawk 4和Pixhawk 4 Mini的PWM输出端口。

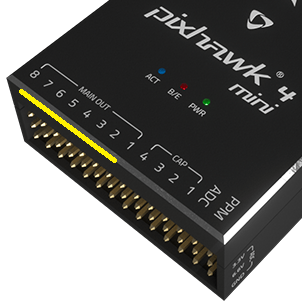
输出分为 MAIN 和 AUX,并单独编号(MAINn 和 AUXn, n 通常是从1到6或8)。 They might also be marked as IO PWM Out and FMU PWM OUT (or similar).
注意
A flight controller may only have MAIN PWM outputs (like the Pixhawk 4 Mini), or may have only 6 outputs on either MAIN or AUX. Ensure that you select a controller that has enough ports/outputs for your airframe.
You can connect almost any output to any motor or other actuator, by assigning the associated function ("Motor 1") to the desired output ("AUX1") in QGroundControl: Actuator Configuration and Testing. Note that the functions (motor and control surface actuator positions) for each frame are given in the Airframe Reference.
备注:
- Pixhawk controllers have an FMU board and may have a separate IO board. 如果有IO 板,
AUX端口直接连接到 FMU 和MIAN端口连接到IO板。 否则,MAIN端口连接到FMU,没有AUX端口。 - The FMU output ports can use D-shot or One-shot protocols (as well as PWM), which provide much lower-latency behaviour. 这对于竞速机和其他需要更好性能的机体来说是有用的。
MAIN和AUX中仅有6-8个输出,因为大多数飞行控制器只有这么多的 PWM/Dshot/Oneshot 输出。 理论上来说,如果总线支持,可以有更多的输出(比如UAVCAN总线就不限于这几个节点)。
# 电调 & 电机
Many PX4 drones use brushless motors that are driven by the flight controller via an Electronic Speed Controller (ESC) (the ESC converts a signal from the flight controller to an appropriate level of power delivered to the motor).
有关 PX4 支持的电调和电机的信息,请参阅:
- 电调 & 电机
- 电调(ESC)校准
- 电调固件和协议概述 (opens new window)(oscarliang.com)
# 电池/电源
PX4无人机最常使用的是锂聚合物(LiPo)电池。 The battery is typically connected to the system using a Power Module or Power Management Board, which provide separate power for the flight controller and to the ESCs (for the motors).
Information about batteries and battery configuration can be found in Battery Configuration and the guides in Basic Assembly (e.g. Pixhawk 4 Wiring Quick Start > Power).
# Manual Control
Pilots can control a vehicle manually using either a Radio Control (RC) System or a Joystick/Gamepad controller connected via QGroundControl.
PX4 does not _require_ a manual control system for autonomous flight modes.
注解
Both methods can be used for most manual control use cases, such as surveys. RC systems are recommended when first tuning/testing a new frame design or when flying racers/acrobatically (and in other cases where low latency is important).
# 无线电控制(遥控)
Radio Control (RC) systems can be used to manually control PX4.
They consist of a ground based RC controller that uses a radio transmitter to communicate stick/control positions to a receiver on the vehicle. 一些遥控系统还可以额外接收自动驾驶仪传回的数传信息。

遥控系统选择解释了如何选择遥控系统。 其他相关主题包括:
- Radio/Remote Control Setup - Remote control configuration in QGroundControl.
- Manual Flying - Learn how to fly with a remote control.
- FrSky 数传 - 设置遥控发射机以从 PX4 接收数传/状态更新。
# 地面站游戏手柄控制器
A Joystick/Gamepad connected through QGroundControl can also be used to manually control PX4.
With this approach, QGroundControl translates stick/button information from a connected Joystick into MAVLink-protocol messages, which are then sent to PX4 using the shared telemetry radio link. The telemetry radio must have sufficient bandwidth for both manual control and other telemetry messages, and of course this approach means that you must have a ground station running QGroundControl.
Joysticks are also used to manually fly PX4 in a simulator.
注解
Controllers like the Auterion Skynav (opens new window) and UAVComponents MicroNav (opens new window) integrate QGC and a Joystick, and connect the vehicle via a high bandwidth telemetry radio link.

# 安全开关
Some vehicles have a safety switch that must be engaged before the vehicle can be armed (when armed, motors are powered and propellers can turn).
通常,安全开关被整合到GPS设备中,但也可能是一个单独的物理组件。
# 数传电台
Data/Telemetry Radios can provide a wireless MAVLink connection between a ground control station like QGroundControl and a vehicle running PX4. 这使得在飞行过程中调整参数,实时监视遥测信息,更改任务等成为可能。
# 机载计算机
A Companion Computer (also referred to as "mission computer" or "offboard computer"), is a separate on-vehicle computer that communicates with PX4 to provide higher level command and control.
The companion computer usually runs Linux, as this is a much better platform for "general" software development, and allows drones to leverage pre-existing software for computer vision, networking, and so on.
The flight controller and companion computer may be pre-integrated into a single baseboard, simplifying hardware development, or may be separate, and are connected via a serial cable, Ethernet cable, or wifi. The companion computer typically communicates with PX4 using a high level Robotics API such as MAVSDK (opens new window) or ROS 2.
Relevant topics include:
- Companion Computers
- Offboard 模式 - 用于从地面站或机载计算机对 PX4 进行 Offboard 控制的飞行模式。
- 机器人(Robotics) APIs
# SD卡(可移除储存器)
PX4 使用 SD 储存卡存储 飞行日志,而且还需要内存卡才能使用 UAVCAN 外围设备,运行 飞行任务。
默认情况下,如果没有 SD 卡,PX4 将在启动时播放 格式化失败(2-声短响) 两次(且上述需要储存卡的功能都不可用)。
提示
Pixhawk 飞控板支持的最大 SD 卡大小为 32 GB 。 The SanDisk Extreme U3 32GB is highly recommended.
尽管如此,SD卡也只是可选的。 不包含 SD 卡槽的飞行控制器可以:
- 使用参数 CBRK_BUZZER 禁用通知蜂鸣器。
- 推流日志 到另一个组件(机载计算机)。
- Store missions in RAM/FLASH.
# 解锁和加锁
A vehicle is said to be armed when all motors and actuators are powered, and disarmed when nothing is powered. There is also a prearmed state when only actuators are powered.
注意
Armed vehicles can be dangerous as propellors will be spinning.
Arming is triggered by default (on Mode 2 transmitters) by holding the RC throttle/yaw stick on the bottom right for one second (to disarm, hold stick on bottom left). 还可以使用遥控上的按钮来配置 PX4 解锁(也可以从地面站发送MAVLink解锁命令)。
To reduce accidents, vehicles should be armed as little as possible when the vehicle is on the ground. By default, vehicles are:
- Disarmed or Prearmed (motors unpowered) when not in use, and must be explicitly armed before taking off.
- Automatically disarm/prearm if the vehicle does not take off quickly enough after arming (the disarm time is configurable).
- Automatically disarm/prearm shortly after landing (the time is configurable).
- 载具如果不是在“健康”状态,则会解锁不通过。
- Arming is prevented if the vehicle has a safety switch that has not been engaged.
- 如果VTOL飞行器处于固定翼飞机模式,则阻止解锁(默认情况下)。
When prearmed you can still use actuators, while disarming unpowers everything. Prearmed and disarmed should both safe, and a particular vehicle may support either or both.
提示
Sometimes a vehicle will not arm for reasons that are not obvious. QGC v4.2.0 (Daily build at time of writing) and later provide an arming check report in Fly View > Arming and Preflight Checks (opens new window). From PX4 v1.14 this provides comprehensive information about arming problems along with possible solutions.
更详细的解锁和加锁的配置的解读可以在这里找到:预解锁,解锁,加锁配置。
# 飞行模式
Flight modes provide different types/levels of vehicle automation and autopilot assistance to the user (pilot). Autonomous modes are fully controlled by the autopilot, and require no pilot/remote control input. These are used, for example, to automate common tasks like takeoff, returning to the home position, and landing. Other autonomous modes execute pre-programmed missions, follow a GPS beacon, or accept commands from an offboard computer or ground station.
Manual modes are controlled by the user (via the RC control sticks/joystick) with assistance from the autopilot. Different manual modes enable different flight characteristics - for example, some modes enable acrobatic tricks, while others are impossible to flip and will hold position/course against wind.
提示
Not all flight modes are available on all vehicle types, and some modes can only be used when specific conditions have been met (e.g. many modes require a global position estimate).
An overview of the available flight modes can be found here. Instructions for how to set up your remote control switches to turn on different flight modes is provided in Flight Mode Configuration.
# 安全设置(故障保护)
PX4 has configurable failsafe systems to protect and recover your vehicle if something goes wrong! These allow you to specify areas and conditions under which you can safely fly, and the action that will be performed if a failsafe is triggered (for example, landing, holding position, or returning to a specified point).
注解
You can only specify the action for the first failsafe event. Once a failsafe occurs the system will enter special handling code, such that subsequent failsafe triggers are managed by separate system level and vehicle specific code.
The main failsafe areas are listed below:
- Low Battery
- Remote Control (RC) Loss
- Position Loss (global position estimate quality is too low).
- Offboard Loss (e.g. lose connection to companion computer)
- Data Link Loss (e.g. lose telemetry connection to GCS).
- Geofence Breach (restrict vehicle to flight within a virtual cylinder).
- Mission Failsafe (prevent a previous mission being run at a new takeoff location).
- Traffic avoidance (triggered by transponder data from e.g. ADSB transponders).
For more information see: Safety (Basic Configuration).
# 航向和运动方向
All the vehicles, boats and aircraft have a heading direction or an orientation based on their forward motion.
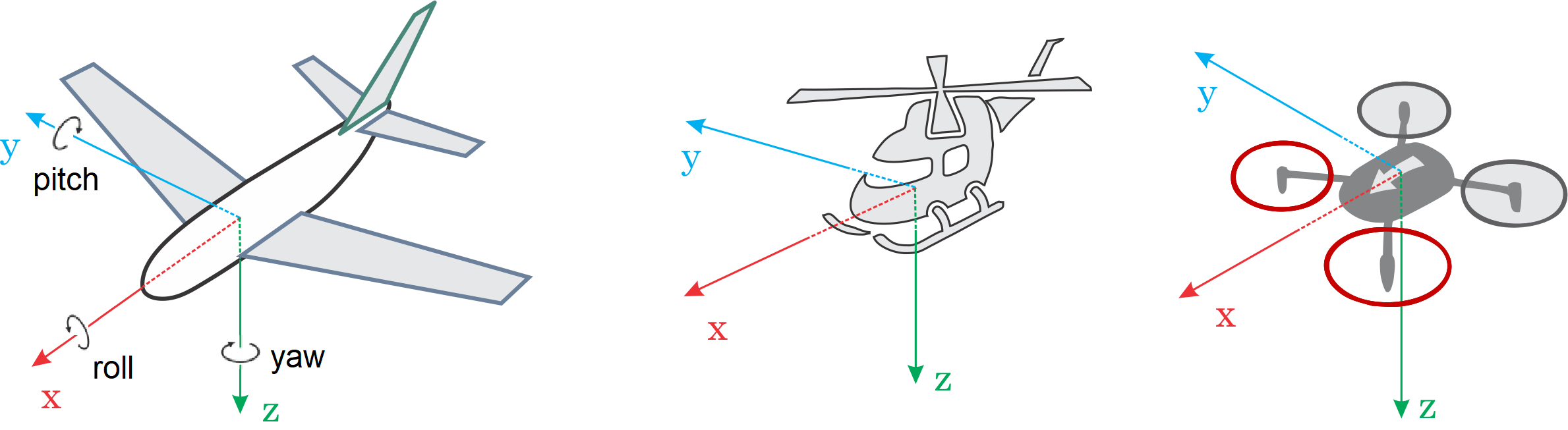
注解
For a VTOL Tailsitter the heading is relative to the multirotor configuration (i.e. vehicle pose during takeoff, hovering, landing).
It is important to know the vehicle heading direction in order to align the autopilot with the vehicle vector of movement. Multicopters have a heading even when they are symmetrical from all sides! Usually manufacturers use a colored props or colored arms to indicate the heading.
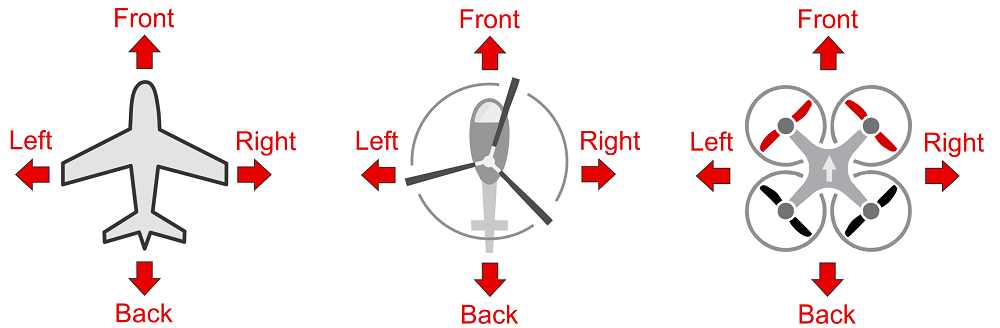
In our illustrations we will use red coloring for the front propellers of multicopter to show heading.
You can read in depth about heading in Flight Controller Orientation