ROS with Gazebo Classic Simulation
ROS (Robot Operating System) can be used with PX4 and the Gazebo Classic simulator. It uses the MAVROS MAVLink node to communicate with PX4.
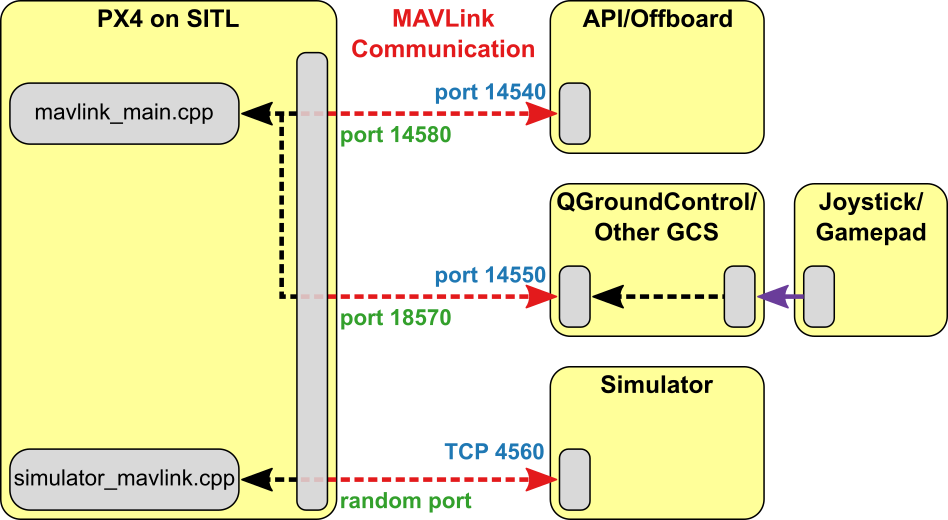
The ROS/Gazebo Classic integration with PX4 follows the pattern in the diagram below (this shows the generic PX4 simulation environment). PX4 communicates with the simulator (e.g. Gazebo Classic) to receive sensor data from the simulated world and send motor and actuator values. It communicates with the GCS and an Offboard API (e.g. ROS) to send telemetry from the simulated environment and receive commands.
INFO
The only slight difference to "normal behaviour" is that ROS initiates the connection on port 14557, while it is more typical for an offboard API to listen for connections on UDP port 14540.
Installing ROS and Gazebo Classic
ROS (1) with MAVROS Installation Guide explains how to set up a guide for working with ROS (1), MAVROS, and PX4.
INFO
ROS is only supported on Linux (not macOS or Windows).
Launching ROS/Simulation
The command below can be used to launch the simulation and connect ROS to it via MAVROS, where fcu_url is the IP / port of the computer running the simulation:
sh
roslaunch mavros px4.launch fcu_url:="udp://:14540@192.168.1.36:14557"To connect to localhost, use this URL:
sh
roslaunch mavros px4.launch fcu_url:="udp://:14540@127.0.0.1:14557"INFO
It can be useful to call roslaunch with the -w NUM_WORKERS (override number of worker threads) and/or -v (verbose) in order to get warnings about missing dependencies in your setup. For example:
sh
roslaunch mavros px4.launch fcu_url:="udp://:14540@127.0.0.1:14557"Launching Gazebo Classic with ROS Wrappers
The Gazebo Classic simulation can be modified to integrate sensors publishing directly to ROS topics e.g. the Gazebo Classic ROS laser plugin. To support this feature, Gazebo Classic must be launched with the appropriate ROS wrappers.
There are ROS launch scripts available to run the simulation wrapped in ROS:
- posix_sitl.launch: plain SITL launch
- mavros_posix_sitl.launch: SITL and MAVROS
To run SITL wrapped in ROS the ROS environment needs to be updated, then launch as usual:
(optional): only source the catkin workspace if you compiled MAVROS or other ROS packages from source:
sh
cd <PX4-Autopilot_clone>
DONT_RUN=1 make px4_sitl_default gazebo-classic
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash # (optional)
source Tools/simulation/gazebo-classic/setup_gazebo.bash $(pwd) $(pwd)/build/px4_sitl_default
export ROS_PACKAGE_PATH=$ROS_PACKAGE_PATH:$(pwd)
export ROS_PACKAGE_PATH=$ROS_PACKAGE_PATH:$(pwd)/Tools/simulation/gazebo-classic/sitl_gazebo-classic
roslaunch px4 posix_sitl.launchInclude one of the above mentioned launch files in your own launch file to run your ROS application in the simulation.
What's Happening Behind the Scenes
This section shows how the roslaunch instructions provided previously actually work (you can follow them to manually launch the simulation and ROS).
You will need three terminals, in all of them the ros environment must be sourced.
First start the simulator using the command below:
sh
cd <PX4-Autopilot_clone>
export ROS_PACKAGE_PATH=$ROS_PACKAGE_PATH:$(pwd)
roslaunch px4 px4.launchThe console will look like this:
sh
INFO [px4] instance: 0
______ __ __ ___
| ___ \ \ \ / / / |
| |_/ / \ V / / /| |
| __/ / \ / /_| |
| | / /^\ \ \___ |
\_| \/ \/ |_/
px4 starting.
INFO [px4] startup script: /bin/sh etc/init.d-posix/rcS 0
INFO [init] found model autostart file as SYS_AUTOSTART=10016
INFO [param] selected parameter default file parameters.bson
INFO [param] importing from 'parameters.bson'
INFO [parameters] BSON document size 295 bytes, decoded 295 bytes (INT32:12, FLOAT:3)
INFO [param] selected parameter backup file parameters_backup.bson
INFO [dataman] data manager file './dataman' size is 7866640 bytes
etc/init.d-posix/rcS: 31: [: Illegal number:
INFO [init] PX4_SIM_HOSTNAME: localhost
INFO [simulator_mavlink] Waiting for simulator to accept connection on TCP port 4560In the second terminal make sure you will be able to start gazebo with the world files defined in PX4-Autopilot. To do this set your environment variables to include the appropriate sitl_gazebo-classic folders.
sh
cd <PX4-Autopilot_clone>
source Tools/simulation/gazebo-classic/setup_gazebo.bash $(pwd) $(pwd)/build/px4_sitl_default
export ROS_PACKAGE_PATH=$ROS_PACKAGE_PATH:$(pwd)/Tools/simulation/gazebo-classic/sitl_gazebo-classicNow start Gazebo Classic like you would when working with ROS
sh
roslaunch gazebo_ros empty_world.launch world_name:=$(pwd)/Tools/simulation/gazebo-classic/sitl_gazebo-classic/worlds/empty.worldIn the third terminal make sure you will be able to spawn the model with the sdf files defined in PX4-Autopilot. To do this set your environment variables to include the appropriate sitl_gazebo-classic folders.
sh
cd <PX4-Autopilot_clone>
source Tools/simulation/gazebo-classic/setup_gazebo.bash $(pwd) $(pwd)/build/px4_sitl_default
export ROS_PACKAGE_PATH=$ROS_PACKAGE_PATH:$(pwd)/Tools/simulation/gazebo-classic/sitl_gazebo-classicNow insert the Iris quadcopter model like you would when working with ROS. Once the Iris is loaded it will automatically connect to the px4 app.
sh
rosrun gazebo_ros spawn_model -sdf -file $(pwd)/Tools/simulation/gazebo-classic/sitl_gazebo-classic/models/iris/iris.sdf -model iris -x 0 -y 0 -z 0 -R 0 -P 0 -Y 0