Visual Inertial Odometry (VIO)
视觉惯性里程计测距(VIO)是一种计算机视觉技术,用于估算3D姿态(local 位置和方向),相对于 local 起始位置的移动的机体 速度。 它通常用于在GPS不存在或不可靠的情况下(例如室内或在桥下飞行时)给载具导航。
VIO使用视觉测距法从相机图像中估计机身姿态,并结合机身IMU的惯性测量(以校正因不良的图像捕获导致的机身快速移动的错误)。
This topic gives guidance on configuring PX4 and a companion computer for a VIO setup.
The suggested setup uses ROS for routing VIO information to PX4. However, PX4 itself does not care about the source of messages, provided they are provided via the appropriate MAVLink Interface.
Suggested Setup
A hardware and software setup for VIO is suggested in the sections below as an illustration of how to interface a VIO system with PX4. It makes use of an off-the-shelf tracking camera and a companion computer running ROS. ROS is used to read odometry information from the camera and supply it to PX4.
An example of a suitable tracking camera is the Intel® RealSense™ Tracking Camera T265.
相机安装
将相机连接到机载计算机并将其安装到机架上:
- 尽可能使镜头朝下安装相机(默认)。
- Cameras are typically very sensitive to vibration; a soft mounting is recommended (e.g. using vibration isolation foam).
Companion Setup
To setup ROS and PX4:
- 在机载计算机上安装和配置 MAVROS。
- Implement and run a ROS node to read data from the camera and publish the VIO odometry using MAVROS.
- See the VIO ROS node section below for details of the requirements for this node.
- 按照下方的说明调整 PX4 EKF2 估计器。
- 验证与飞控的连接。
TIP
您可以使用*QGroundControl * 中的 MAVLink Inspector来验证是否收到ODOMETRY或VISION_POSITION_ESTIMATE消息(或检查是否存在 HEARTBEAT消息,其组件ID为197(MAV_COMP_ID_VISUAL_INERTIAL_ODOMETRY)。
- Verify that VIO is set up correctly before your first flight!
ROS VIO node
In this suggested setup, a ROS node is required to
- interface with the chosen camera or sensor hardware,
- produce odometry messages containing the position estimate, which will be sent to PX4 using MAVROS, and
- publish messages to indicate the VIO system status.
The implementation of the ROS node will be specific to the camera used and will need to be developed to use the interface and drivers appropriate for the camera.
The odometry messages should be of the type nav_msgs/Odometry and published to the topic /mavros/odometry/out.
System status messages of the type mavros_msgs/CompanionProcessStatus should be published to the topic /mavros/companion_process/status. These should identify the component as MAV_COMP_ID_VISUAL_INERTIAL_ODOMETRY (197) and indicate the state of the system. Recommended status values are:
MAV_STATE_ACTIVEwhen the VIO system is functioning as expected,MAV_STATE_CRITICALwhen the VIO system is functioning, but with low confidence, andMAV_STATE_FLIGHT_TERMINATIONwhen the system has failed or the estimate confidence is unacceptably low.
PX4 调试
将相机连接到机载计算机并将其安装到框架:
| 参数 | 外部位置估计的设置 |
|---|---|
| EKF2_EV_CTRL | Set horizontal position fusion, vertical vision fusion, velocity fusion, and yaw fusion according to your desired fusion model. |
| EKF2_HGT_REF | 设置为 Vision 以使用视觉作为高度估计的主要来源。 |
| EKF2_EV_DELAY | 设置为测量的时间戳和 "实际" 捕获时间之间的差异。 有关详细信息,请参阅 below。 |
| EKF2_EV_POS_X, EKF2_EV_POS_Y, EKF2_EV_POS_Z | Set the position of the vision sensor with respect to the vehicle's body frame. |
这些参数可以在QGroundControl>Vehicle Setup > Parameters > EKF2中设置(切记要使参数更改生效需要重启飞控)。
更多详情/附加信息,见: ECL/EKF 概述 & 调试 > 外部视觉系统。
EKF2_EV_DELAY 调参
EKF2_EV_DELAY is the Vision Position Estimator delay relative to IMU measurements. 换而言之,这是视觉系统时间戳和 IMU 时钟( EKF2 “时基” )记录的“实际”捕获时间之间的差异。
Technically this can be set to 0 if there is correct timestamping (not just arrival time) and timesync (e.g. NTP) between MoCap and (for example) ROS computers. 实际应用中,这可能需要进行一些基于经验的调整,因为通信链路中的延迟与具体设置非常相关。 It is rare that a system is set up with an entirely synchronised chain!
通过检查 IMU 速率和 EV 速率之间的偏移,可以从日志中获取对延迟的粗略估计:
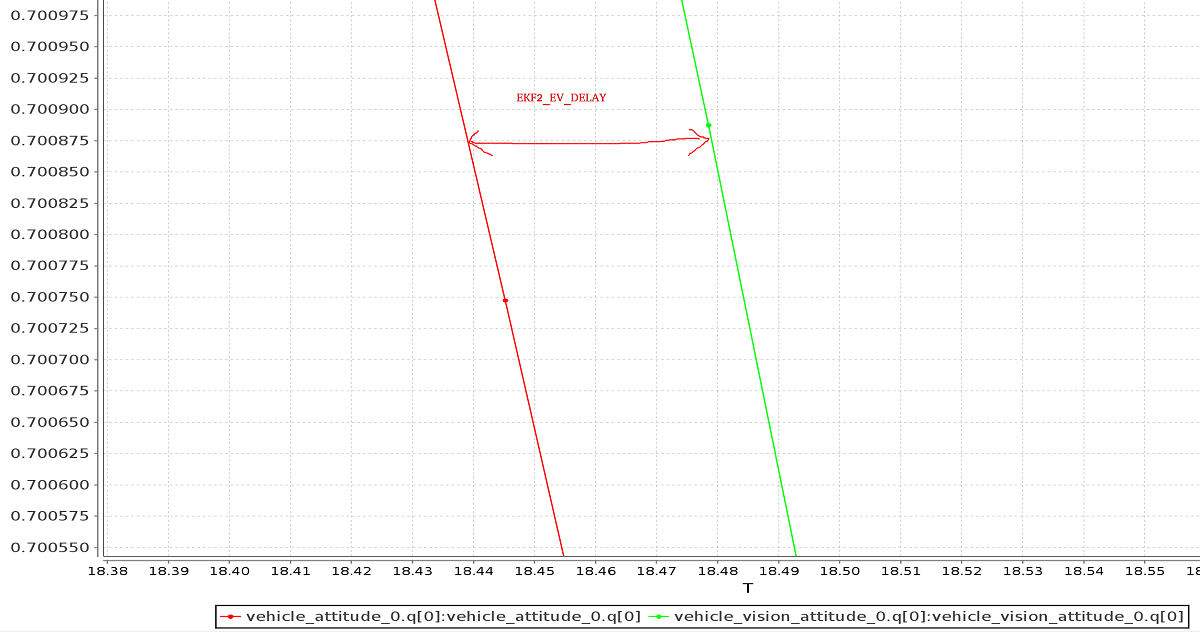
TIP
注意 可以使用 FlightPlot 或类似的飞行分析工具生成一组外部数据与板载估计(如上)。
可以通过更改参数来进一步调整该值,以找到在动态变化中最低的 EKF 更新值。
检查/校验 VIO 估计
The MAV_ODOM_LP parameter mentioned below was removed in PX4 v1.14. This section needs to be updated.
执行以下检查,以确保在首次飞行之前 VIO 正常运行:
- 设置 PX4 参数
MAV_ODOM_LP为1。 然后PX4将接收到的外部姿态用MAVLinkODOMETRY消息回传。 您可以使用 QGroundControl 中的 MAVLink Inspector 查看这些MAVLink 消息。 - 偏航机身,直到
ODOMETRY消息的四元数非常接近单位四元数(w = 1,x = y = z = 0)。- At this point, the body frame is aligned with the reference frame of the external pose system.
- 如果在不使横滚或俯仰的情况下无法使四元数接近单位四元数,则机架可能仍存在俯仰或滚动偏移。 这种情况下不要再检查机架坐标系。
- Once aligned, you can pick the vehicle up from the ground and you should see the position's z coordinate decrease. Moving the vehicle in the forward direction should increase the position's x coordinate. Moving the vehicle to the right should increase the y coordinate.
- Check that linear velocities in the message are expressed in the FRD body frame reference frame.
- 设置 PX4 参数
MAV_ODOM_LP为 0。 PX4 将停止ODOMETRY消息回传。
可以通过更改参数来进一步调整该值,以找到在动态变化中最低的EKF更新值。
将无人机放在地面上,并开始流式传输
ODOMETRY反馈(如上所述)。 油门杆推到最低并解锁。此时,设置为位置控制模式。 如果切换成功,飞控会闪绿灯。 绿灯代表:你的外部位置信息已经注入到飞控中,并且位置控制模式已经切换成功。
油门杆放到中间位置(死区),以便无人机保持飞行高度。 提高操控杆会增加参考高度,降低操控杆会降低参考高度。 Similarly, the other stick will change the position over the ground.
Increase the value of the throttle stick and the vehicle will take off. Move it back to the middle immediately afterwards.
确保无人机可以保持位置。
故障处理
First, make sure MAVROS is able to connect successfully to the flight controller.
如果连接正确, 常见问题 / 解决方案是:
问题: 当无人机飞行时发生漂移/飞走,但是当拿掉螺旋桨时不会发生漂移。
- If using the T265 try soft-mounting it (this camera is very sensitive to high-frequency vibrations).
问题: 启用 VIO 时产生了马桶效应。
- 确保相机的方向与启动文件中的变换匹配。 使用 QGroundControl 中的 MAVLink Inspector 验证来自 MAVROS 的
ODOMETRY消息中的速度是否与 FRD (前右下)坐标系一致。
- 确保相机的方向与启动文件中的变换匹配。 使用 QGroundControl 中的 MAVLink Inspector 验证来自 MAVROS 的
问题: 想使用视觉位置来做闭环,也想运行 GPS 。
- 这确实很困难,因为当他们不同意时,就会混淆 EKF。 通过测试,仅使用视觉速度更为可靠(如果您想出一种使该配置可靠的方法,请告诉我们)。
开发人员信息
对扩展此实现感兴趣的开发人员(或编写另一种不依赖 ROS 的实现)应该看看 使用视觉或运动捕获系统进行位置估计。
本主题还说明了如何配置 VIO 来配合 LPE 估计器 一起使用(不推荐)。