多旋翼PID调参(手动/高级)
本主题提供有关 PX4 控制器以及如何调参的详细信息。
TIP
Autotune is recommended for tuning the vehicles around the hover thrust point, as the approach described is intuitive, easy, and fast. 这就是许多机体所需要的全部。
当调整悬停推力点不足时使用自动调参(例如,在机体上,在更高推力时存在非线性和振荡)。 It is also useful for a deeper understanding of how the basic tuning works, and to understand how to use the airmode setting.
调参步骤
INFO
For safety reasons, the default gains are set to low values. 您必须增加增益才能得到良好的控制响应。
以下是做调参时要遵循的一些要点:
- 调整增益时,所有的增益值都应该慢慢增加, 因为增益过大可能会导致危险的振荡! 一般情况下,每次增益值的调整幅度大约在20%到30%,获得最优增益值后,基于最优值再下调5%到10%。
- 在修改参数之前务必先着陆。 慢慢增加油门,观察振荡的现象。
- Tune the vehicle around the hovering thrust point, and use the thrust curve parameter to account for thrust non-linearities or high-thrust oscillations.
- Optionally enable the high-rate logging profile with the SDLOG_PROFILE parameter so you can use the log to evaluate the rate and attitude tracking performance (the option can be disabled afterwards).
WARNING
Always disable MC_AIRMODE when tuning a vehicle.
角速度控制器
The rate controller is the inner-most loop with three independent PID controllers to control the body rates (roll, pitch, yaw).
INFO
A well-tuned rate controller is very important as it affects all flight modes. A badly tuned rate controller will be visible in Position mode, for example, as "twitches" or oscillations (the vehicle will not hold perfectly still in the air).
速率控制器架构/形式
PX4 supports two (mathematically equivalent) forms of the PID rate controller in a single "mixed" implementation: Parallel and Standard.
Users can select the form that is used by setting the proportional gain for the other form to "1" (i.e. in the diagram below set K to 1 for the parallel form, or P to 1 for the standard form - this will replace either the K or P blocks with a line).
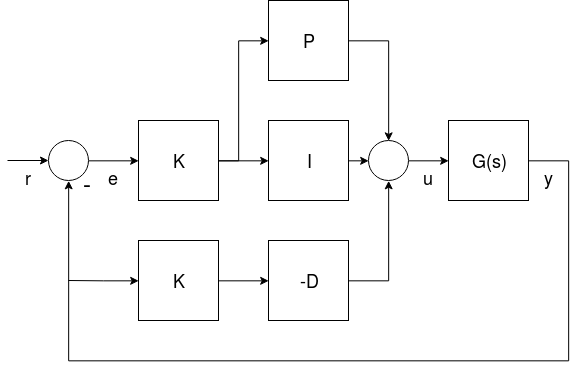
- G(s) represents the angular rates dynamics of a vehicle
- r is the rate setpoint
- y is the body angular rate (measured by a gyro)
- e is the error between the rate setpoint and the measured rate
- u is the output of the PID controller
这两种形式将在后面介绍。
INFO
The derivative term (D) is on the feedback path in order to avoid an effect known as the derivative kick.
TIP
有关详细信息,请参阅︰
- Not all PID controllers are the same (www.controleng.com)
- PID controller > Standard versus parallel (ideal) PID form (Wikipedia)
并行模式
The parallel form is the simplest form, and is (hence) commonly used in textbooks. 在这种情况下,控制器的输出只是简单的将比例,积分和微分项相加。
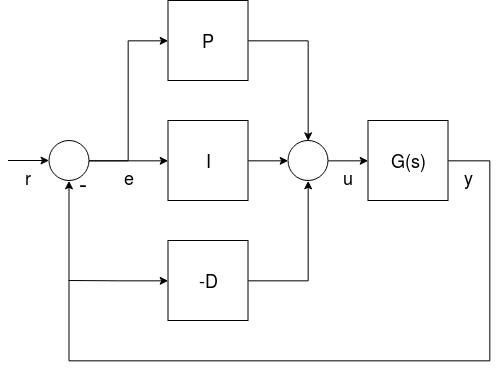
标准模式
这种形式在数学上等同于并行形式。 但主要的优点是(即使似乎有点反直觉)将比例增益的调试与积分、微分增益分离开了。 这意味着一个新的平台通过使用同样大小/推力 无人机的增益,使它更易于调试,只是简单地调整K增益就可正常飞行。
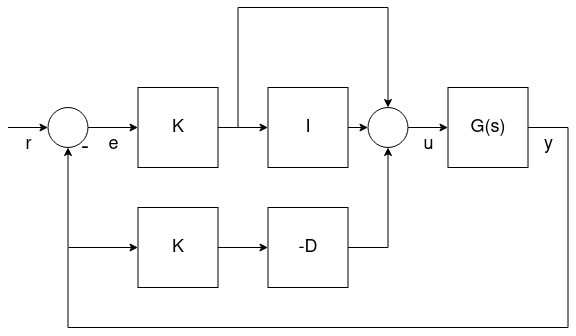
角速度 PID 调试
调试角速度PID控制器的相关参数是:
- Roll rate control (MC_ROLLRATE_P, MC_ROLLRATE_I, MC_ROLLRATE_D, MC_ROLLRATE_K)
- Pitch rate control (MC_PITCHRATE_P, MC_PITCHRATE_I, MC_PITCHRATE_D, MC_PITCHRATE_K)
- Yaw rate control (MC_YAWRATE_P, MC_YAWRATE_I, MC_YAWRATE_D, MC_YAWRATE_K)
The rate controller can be tuned in Acro mode or Stabilized mode:
Acro mode is preferred because it allows for isolated rate control testing. However it is significantly harder to pilot.
WARNING
If you choose this mode, you must disable all stick expo and have reasonable maximum rates for all axes:
MC_ACRO_EXPO= 0,MC_ACRO_EXPO_Y= 0,MC_ACRO_SUPEXPO= 0,MC_ACRO_SUPEXPOY= 0MC_ACRO_P_MAX= 200,MC_ACRO_R_MAX= 200MC_ACRO_Y_MAX= 100
For PX4 v1.15 and later the defaults are set for this purpose to a maximum rate of 100°/s linear mapping for all axes.
:::
- Stabilized mode is simpler to fly, but it is also much more difficult to distinguish if attitude or rate controller causes a certain behavior.
万一你的飞行器完全飞不起来:
- If there are strong oscillations when first trying to takeoff (to the point where it does not fly), decrease all P and D gains until it takes off.
- If the reaction to RC movement is minimal, increase the P gains.
The actual tuning is roughly the same in Manual mode or Acro mode: You iteratively tune the P and D gains for roll and pitch, and then the I gain. 一开始你的ROLL和PITCH可以用相同的值,等调的差不多了,细调的时候可以分别再调整滚转和俯仰(如果你的飞行器是对称的,那就不用再细调了。) For yaw it is very similar, except that D can be left at 0.
比例增益 (P/K)
The proportional gain is used to minimize the tracking error (below we use P to refer to both P or K). 它可以加快响应速度,因此应该在不引入震荡的前提下设的尽量的高。
- If the P gain is too high: you will see high-frequency oscillations.
- If the P gain is too low:
- 飞行器会对遥控器的输入很迟钝。
- In Acro mode the vehicle will drift, and you will constantly need to correct to keep it level.
微分增益 (D)
The D (derivative) gain is used for rate damping. 同样地,这个值应该尽量设大一些来避免超调。
- If the D gain is too high: the motors become twitchy (and maybe hot), because the D term amplifies noise.
- If the D gain is too low: you see overshoots after a step-input.
典型值是:
- standard form (P = 1): between 0.01 (4" racer) and 0.04 (500 size), for any value of K
- parallel form (K = 1): between 0.0004 and 0.005, depending on the value of P
积分增益 (I)
The I (integral) gain keeps a memory of the error. The I term increases when the desired rate is not reached over some time. It is important (especially when flying Acro mode), but it should not be set too high.
- 如果积分增益太高:你会看到缓慢的振荡。
- If the I gain is too low: this is best tested in Acro mode, by tilting the vehicle to one side about 45 degrees, and keeping it like that. 他应该始终保持相同的角度。 If it drifts back, increase the I gain. A low I gain is also visible in a log, when there is an offset between the desired and the actual rate over a longer time.
典型值是:
- standard form (P = 1): between 0.5 (VTOL plane), 1 (500 size) and 8 (4" racer), for any value of K
- parallel form (K = 1): between 0.3 and 0.5 if P is around 0.15 The pitch gain usually needs to be a bit higher than the roll gain.
测试步骤
To test the current gains, provide a fast step-input when hovering and observe how the vehicle reacts. 他应该反应很快,振荡和超调量都不大。(有种「锁定」的感觉)。
比如在横滚方向上来一个阶跃输入,把横滚杆推向一侧,然后让它迅速回中(注意如果你直接松手的话,由于它的弹簧结构,杆会振荡 - 调好的无人机会跟随这些振荡)。
INFO
A well-tuned vehicle in Acro mode will not tilt randomly towards one side, but keeps the attitude for tens of seconds even without any corrections.
日志
看看日志有助于你看看你调的参咋样。 下面是一份调得比较好的滚转和偏航角速度的日志。
![]()
![]()
下面这份日志的滚转角速度调试的很好,它有几个翻转,也就是很极限的阶跃输入。 You can see that the vehicle overshoots only by a very small amount: ![]()
角度控制
角度控制环控制机体的姿态角,并通过以下参数输出目标角速度:
- Roll control (MC_ROLL_P)
- Pitch control (MC_PITCH_P)
- Yaw control (MC_YAW_P)
姿态角控制环调起来就容易多了。 其实大多数时候默认值就够了,完全不用调。
To tune the attitude controller, fly in Stabilized mode and increase the P gains gradually. 如果看到有振荡或者超调,就说明增益调得太高了。
下面这几个参数也可以调整 这些参数决定了绕三个轴的最大角速度:
- Maximum roll rate (MC_ROLLRATE_MAX)
- Maximum pitch rate (MC_PITCHRATE_MAX)
- Maximum yaw rate (MC_YAWRATE_MAX)
推力曲线
以上的调整都是在悬停油门的基础上的。 但当你逐渐增大到满油门时,机体可能又开始振荡了。
To counteract that, adjust the thrust curve with the THR_MDL_FAC parameter.
INFO
The rate controller might need to be re-tuned if you change this parameter.
The mapping from motor control signals (e.g. PWM) to expected thrust is linear by default — setting THR_MDL_FAC to 1 makes it quadratic. Values in between use a linear interpolation of the two. Typical values are between 0.3 and 0.5.
If you have a thrust stand (or can otherwise measure thrust and motor commands simultaneously), you can determine the relationship between the motor control signal and the motor's actual thrust, and fit a function to the data. The motor command in PX4 called actuator_output can be PWM, Dshot, UAVCAN commands for the respective ESCs in use. This Notebook shows one way for how the thrust model factor THR_MDL_FAC may be calculated from previously measured thrust and PWM data. The curves shown in this plot are parametrized by both α and k, and also show thrust and PWM in real units (kgf and μs). In order to simplify the curve fit problem, you can normalize the data between 0 and 1 to find k without having to estimate α (α = 1, when the data is normalized).
]
INFO
The mapping between PWM and static thrust depends highly on the battery voltage.
An alternative way of performing this experiment is to make a scatter plot of the normalized motor command and thrust values, and iteratively tune the thrust curve by experimenting with the THR_MDL_FAC parameter. An example of that graph is shown here:
If raw motor command and thrust data is collected throughout the full-scale range in the experiment, you can normalize the data using the equation:
normalized_value = ( raw_value - min (raw_value) ) / ( max ( raw_value ) - min ( raw_value ) )
After you have a scatter plot of the normalized values, you can try and make the curve match by plotting the equation
_rel_thrust = ( THR_MDL_FAC ) _ rel_signal^2 + ( 1 - THR_MDL_FAC ) * rel_signal*
over a linear range of normalized motor command values between 0 and 1. Note that this is the equation that is used in the firmware to map thrust and motor command, as shown in the THR_MDL_FAC parameter reference. Here, rel_thrust is the normalized thrust value between 0 and 1, and rel_signal is the normalized motor command signal value between 0 and 1.
In this example above, the curve seemed to fit best when THR_MDL_FAC was set to 0.7.
If you don't have access to a thrust stand, you can also tune the modeling factor empirically. Start off with 0.3 and increase it by 0.1 at a time. If it is too high, you will start to notice oscillations at lower throttle values. If it is too low you'll notice oscillations at higher throttle values.
Airmode & Mixer Saturation
The rate controller outputs torque commands for all three axis (roll, pitch and yaw) and a scalar thrust value, which need to be converted into individual motor thrust commands. This step is called mixing.
It can happen that one of the motor commands becomes negative, for example for a low thrust and large roll command (and similarly it can go above 100%). This is a mixer saturation. It is physically impossible for the vehicle to execute these commands (except for reversible motors). PX4 has two modes to resolve this:
Either by reducing the commanded torque for roll such that none of the motor commands is below zero (Airmode disabled). In the extreme case where the commanded thrust is zero, it means that no attitude correction is possible anymore, which is why a minimum thrust is always required for this mode.
Or by increasing (boosting) the commanded thrust, such that none of the motor commands is negative (Airmode enabled). This has the big advantage that the attitude/rates can be tracked correctly even at low or zero throttle. It generally improves the flight performance.
However it increases the total thrust which can lead to situations where the vehicle continues to ascend even though the throttle is reduced to zero. For a well-tuned, correctly functioning vehicle it is not the case, but for example it can happen when the vehicle strongly oscillates due to too high P tuning gains.
Both modes are shown below with a 2D illustration for two motors and a torque command for roll r. On the left motor r is added to the commanded thrust, while on the right motor it is subtracted from it. The motor thrusts are in green. With Airmode enabled, the commanded thrust is increased by b. When it is disabled, r is reduced.
If mixing becomes saturated towards the upper bound the commanded thrust is reduced to ensure that no motor is commanded to deliver more than 100% thrust. This behaviour is similar to the Airmode logic, and is applied whether Airmode is enabled or disabled.
Once your vehicle flies well you can enable Airmode via the MC_AIRMODE parameter.