Multicopter PID Tuning Guide (Manual/Advanced)
PX4 컨트롤러의 튜닝 방법에 대한 자세한 정보를 제공합니다.
TIP
Autotune is recommended for tuning the vehicles around the hover thrust point, as the approach described is intuitive, easy, and fast. 이것은 대부분의 기체에 필요합니다.
호버 추력 지점 주변의 튜닝이 충분하지 않을 때 이 가이드를 사용하십시오 (예 : 더 높은 추력에서 비선형성 및 진동이 방생하는 기체). It is also useful for a deeper understanding of how the basic tuning works, and to understand how to use the airmode setting.
튜닝 단계
INFO
For safety reasons, the default gains are set to low values. 적절한 제어 응답을 얻기 위해서는 게인 값을 적절하게 증가시켜야 합니다.
튜닝시 준수할 일반적인 사항은 아래와 같습니다.
- 큰 이득은 위험한 진동을 발생시킬 수 있으므로, 모든 이득은 매우 천천히 증가시켜야합니다! 일반적으로 반복당 이득을 20~30%씩 증가시키고, 최종 미세 조정을 위해 5~10%로 줄입니다.
- 매개변수를 변경하기 전에 착륙시키십시오. 스로틀을 천천히 증가시키고 진동을 점검하십시오.
- Tune the vehicle around the hovering thrust point, and use the thrust curve parameter to account for thrust non-linearities or high-thrust oscillations.
- Optionally enable the high-rate logging profile with the SDLOG_PROFILE parameter so you can use the log to evaluate the rate and attitude tracking performance (the option can be disabled afterwards).
WARNING
Always disable MC_AIRMODE when tuning a vehicle.
속도 컨트롤러
The rate controller is the inner-most loop with three independent PID controllers to control the body rates (roll, pitch, yaw).
INFO
A well-tuned rate controller is very important as it affects all flight modes. A badly tuned rate controller will be visible in Position mode, for example, as "twitches" or oscillations (the vehicle will not hold perfectly still in the air).
속도 컨트롤러 아키텍처/양식
PX4 supports two (mathematically equivalent) forms of the PID rate controller in a single "mixed" implementation: Parallel and Standard.
Users can select the form that is used by setting the proportional gain for the other form to "1" (i.e. in the diagram below set K to 1 for the parallel form, or P to 1 for the standard form - this will replace either the K or P blocks with a line).
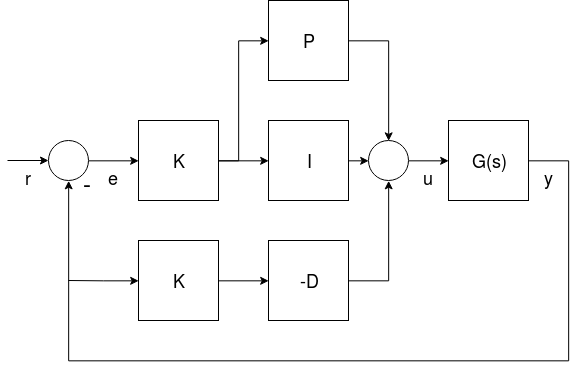
- G(s) represents the angular rates dynamics of a vehicle
- r is the rate setpoint
- y is the body angular rate (measured by a gyro)
- e is the error between the rate setpoint and the measured rate
- u is the output of the PID controller
두 가지 형식이 아래에 기술되어 있습니다.
INFO
The derivative term (D) is on the feedback path in order to avoid an effect known as the derivative kick.
TIP
더 자세한 정보는 다음을 참고하십시오.
- Not all PID controllers are the same (www.controleng.com)
- PID controller > Standard versus parallel (ideal) PID form (Wikipedia)
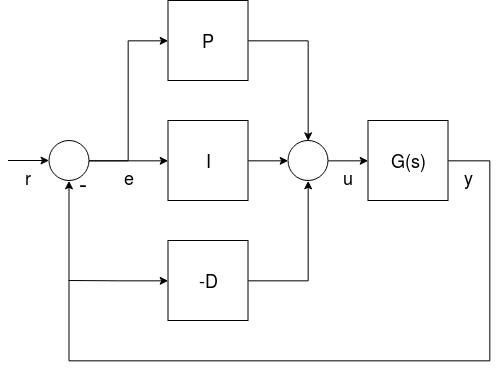
병렬 형식
The parallel form is the simplest form, and is (hence) commonly used in textbooks. 이 경우 컨트롤러의 출력은 간단한 비례, 적분 및 미분 동작의 합입니다.
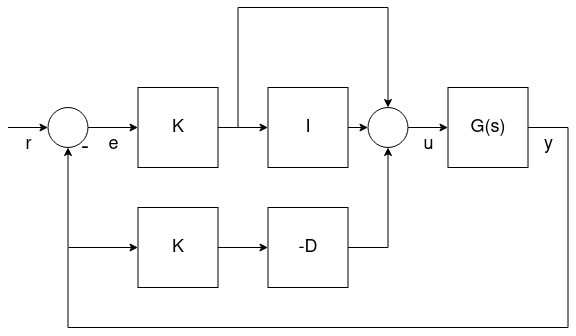
표준 형식
이 형식은 병렬 형식과 수학적으로 동일하지만 주요 이점은 (반 직관적으로 보일지라도) 비례 이득 튜닝을 적분과 미분 이득에서 분리하는 것입니다. 즉, 비슷한 크기와 관성을 가진 드론의 이득을 취하고 K 이득을 조정하여 적절하게 비행하는 방법으로 새로운 플랫폼을 쉽게 조정할 수 있습니다.
속도 PID 튜닝
PID 속도 컨트롤러 튜닝 매개 변수는 다음과 같습니다.
- Roll rate control (MC_ROLLRATE_P, MC_ROLLRATE_I, MC_ROLLRATE_D, MC_ROLLRATE_K)
- Pitch rate control (MC_PITCHRATE_P, MC_PITCHRATE_I, MC_PITCHRATE_D, MC_PITCHRATE_K)
- Yaw rate control (MC_YAWRATE_P, MC_YAWRATE_I, MC_YAWRATE_D, MC_YAWRATE_K)
The rate controller can be tuned in Acro mode or Stabilized mode:
Acro mode is preferred because it allows for isolated rate control testing. However it is significantly harder to pilot.
WARNING
If you choose this mode, you must disable all stick expo and have reasonable maximum rates for all axes:
MC_ACRO_EXPO= 0,MC_ACRO_EXPO_Y= 0,MC_ACRO_SUPEXPO= 0,MC_ACRO_SUPEXPOY= 0MC_ACRO_P_MAX= 200,MC_ACRO_R_MAX= 200MC_ACRO_Y_MAX= 100
For PX4 v1.15 and later the defaults are set for this purpose to a maximum rate of 100°/s linear mapping for all axes.
:::
- Stabilized mode is simpler to fly, but it is also much more difficult to distinguish if attitude or rate controller causes a certain behavior.
기체 비행이 되지 않는 경우:
- If there are strong oscillations when first trying to takeoff (to the point where it does not fly), decrease all P and D gains until it takes off.
- If the reaction to RC movement is minimal, increase the P gains.
The actual tuning is roughly the same in Manual mode or Acro mode: You iteratively tune the P and D gains for roll and pitch, and then the I gain. 처음에는 롤과 피치에 동일한 값을 사용할 수 있으며, 좋은 값을 얻은 후에는 롤과 피치 응답을 개별적으로 확인하여 미세 조정할 수 있습니다 (기체가 대칭인 경우 필요하지 않음). For yaw it is very similar, except that D can be left at 0.
비례 이득 (P/K)
The proportional gain is used to minimize the tracking error (below we use P to refer to both P or K). 빠른 응답을 담당하므로 가능한 높게 설정하여야 하지만, 진동이 발생하지 않아야 합니다.
- If the P gain is too high: you will see high-frequency oscillations.
- If the P gain is too low:
- 기체가 입력 변화에 느리게 반응합니다.
- In Acro mode the vehicle will drift, and you will constantly need to correct to keep it level.
미분 이득 (D)
The D (derivative) gain is used for rate damping. 오버 슈트를 제거하기 위하여 적절하게 높은 값으로 설정합니다.
- If the D gain is too high: the motors become twitchy (and maybe hot), because the D term amplifies noise.
- If the D gain is too low: you see overshoots after a step-input.
일반적인 값은 다음과 같습니다.
- standard form (P = 1): between 0.01 (4" racer) and 0.04 (500 size), for any value of K
- parallel form (K = 1): between 0.0004 and 0.005, depending on the value of P
적분 이득 (I)
The I (integral) gain keeps a memory of the error. The I term increases when the desired rate is not reached over some time. It is important (especially when flying Acro mode), but it should not be set too high.
- I 게인이 너무 높으면 느린 진동이 나타납니다.
- If the I gain is too low: this is best tested in Acro mode, by tilting the vehicle to one side about 45 degrees, and keeping it like that. 같은 각도를 유지하여야 합니다. If it drifts back, increase the I gain. A low I gain is also visible in a log, when there is an offset between the desired and the actual rate over a longer time.
일반적인 값은 다음과 같습니다.
- standard form (P = 1): between 0.5 (VTOL plane), 1 (500 size) and 8 (4" racer), for any value of K
- parallel form (K = 1): between 0.3 and 0.5 if P is around 0.15 The pitch gain usually needs to be a bit higher than the roll gain.
테스트 절차
To test the current gains, provide a fast step-input when hovering and observe how the vehicle reacts. 명령을 즉시 반등하여야 하며, 진동이나 오버슛이 발생하지 않아야 합니다 ( '고정'된 느낌).
예를 들어 롤용 스텝 입력을 만들 수 있습니다. 롤 스틱을 한쪽으로 빠르게 밀었다가 다시 빠르게 놓아줍니다 (스프링이므로 스틱을 놓으면 스틱도 진동합니다. 잘 튜닝된 기체는 이러한 진동에 반응합니다).
INFO
A well-tuned vehicle in Acro mode will not tilt randomly towards one side, but keeps the attitude for tens of seconds even without any corrections.
로그
로그는 추적 성능 평가에 많은 도움이 됩니다. 다음은 롤과 요 속도 추적의 좋은 예입니다.
![]()
![]()
다음은 극단적인 스텝 입력을 생성하는 몇 번의 플립으로 롤 속도를 추적하는 좋은 예입니다. You can see that the vehicle overshoots only by a very small amount: ![]()
자세 컨트롤러
이것은 방향과 아래의 튜닝 매개변수를 사용하여 기체의 비율의 출력을 제어합니다.
- Roll control (MC_ROLL_P)
- Pitch control (MC_PITCH_P)
- Yaw control (MC_YAW_P)
자세 컨트롤러의 튜닝은 비교적 간단합니다. 대부분 기본값을 변경할 필요가 없습니다.
To tune the attitude controller, fly in Stabilized mode and increase the P gains gradually. 진동이나 오버슈트가 나타나는 것은 게인이 너무 높은 것입니다.
아래의 매개변수를 조정할 수 있습니다. 세 축의 최대 회전 속도를 결정합니다.
- Maximum roll rate (MC_ROLLRATE_MAX)
- Maximum pitch rate (MC_PITCHRATE_MAX)
- Maximum yaw rate (MC_YAWRATE_MAX)
추력 곡선
위의 튜닝은 호버 스로틀 주위의 성능을 최적화합니다. 그러나 풀 스로틀로 갈 때 진동이 시작될 수 있습니다.
To counteract that, adjust the thrust curve with the THR_MDL_FAC parameter.
INFO
The rate controller might need to be re-tuned if you change this parameter.
The mapping from motor control signals (e.g. PWM) to expected thrust is linear by default — setting THR_MDL_FAC to 1 makes it quadratic. 그 사이의 값은 둘의 선형 보간을 사용합니다. 일반적인 값은 0.3 ~ 0.5 입니다.
If you have a thrust stand (or can otherwise measure thrust and motor commands simultaneously), you can determine the relationship between the motor control signal and the motor's actual thrust, and fit a function to the data. The motor command in PX4 called actuator_output can be PWM, Dshot, UAVCAN commands for the respective ESCs in use. This Notebook shows one way for how the thrust model factor THR_MDL_FAC may be calculated from previously measured thrust and PWM data. 이 플롯에 표시된 곡선은 α k, 실제 단위 (kgf 및 μs)로 추력과 PWM을 표시합니다. In order to simplify the curve fit problem, you can normalize the data between 0 and 1 to find k without having to estimate α (α = 1, when the data is normalized).
]
INFO
The mapping between PWM and static thrust depends highly on the battery voltage.
An alternative way of performing this experiment is to make a scatter plot of the normalized motor command and thrust values, and iteratively tune the thrust curve by experimenting with the THR_MDL_FAC parameter. 해당 그래프의 예는 아래와 같습니다.
원시 모터 명령 및 추력 데이터가 실험의 전체 범위에 걸쳐 수집되는 경우, 다음 방정식을 사용하여 데이터를 정규화할 수 있습니다.
normalized_value = ( raw_value - min (raw_value) ) / ( max ( raw_value ) - min ( raw_value ) )
정규화된 값의 산점도를 얻은 후 방정식을 플로팅하여 곡선을 일치시킬 수 있습니다.
_rel_thrust = ( THR_MDL_FAC ) _ rel_signal^2 + ( 1 - THR_MDL_FAC ) * rel_signal*
0과 1 사이의 정규화된 모터 명령 값의 선형 범위. Note that this is the equation that is used in the firmware to map thrust and motor command, as shown in the THR_MDL_FAC parameter reference. Here, rel_thrust is the normalized thrust value between 0 and 1, and rel_signal is the normalized motor command signal value between 0 and 1.
In this example above, the curve seemed to fit best when THR_MDL_FAC was set to 0.7.
스러스트 스탠드에 접근할 수 없는 경우, 경험적으로 모델링 요소를 조정할 수 있습니다. 0.3부터 시작하여 한 번에 0.1 씩 늘립니다. 너무 높으면, 낮은 스로틀 값에서 진동이 감지되기 시작합니다. 너무 낮으면, 더 높은 스로틀 값에서 진동이 나타납니다.
Airmode & Mixer Saturation
속도 컨트롤러는 세 축 (roll, pitch 및 yaw)에 대한 토크 명령과 스칼라 추력값을 출력하며, 이는 개별 모터 추력 명령으로 변환하여야 합니다. 이 단계를 믹싱이라고 합니다.
예를 들어 낮은 추력과 큰 롤 명령의 경우 모터 명령 중 하나가 음수가 될 수 있습니다 (비슷하게 100 % 이상이 될 수 있음). 이것은 믹서 포화입니다. 기체가 이 명령을 실행하는 것은 물리적으로 불가능합니다 (가역 모터 제외). PX4에는 이 문제를 해결하기 위한 두 가지 모드가 있습니다.
롤에 대한 명령된 토크를 줄여 모터 명령이 0 미만이 되지 않도록합니다 (에어 모드 비활성화 됨). 명령된 추력이 0 인 극단적인 경우에는 더 이상 자세 보정이 가능하지 않으므로이 모드에 항상 최소 추력이 필요합니다.
또는 명령된 추력을 증가시켜 모터 명령이 음수값이 되지 않도록 합니다(에어 모드 활성화). 이것은 낮은 스로틀이나 제로 스로틀에서도 자세/속도를 정확하게 추적할 수 있는 큰 장점이 있습니다. 일반적으로 비행 성능을 향상시킵니다.
그러나, 이는 스로틀이 0으로 감소하더라도 기체가 계속 상승하도록 총추력을 증가시킵니다. 잘 조정되고 올바르게 작동하는 기체에는 제외하고, 너무 높은 P 조정 이득으로 인하여 기체가 강하게 진동할 때 발생할 수 있습니다.
두 모드는 두 모터에 대한 2D 그림과 롤 r에 대한 토크 명령은 아래에 표시되어 있습니다. 왼쪽 모터에서는 r이 명령된 추력에 추가되고, 오른쪽 모터에서는 차감됩니다. 모터 추력은 녹색입니다. Airmode를 활성화하면 명령된 추력이 b 만큼 증가합니다. 비활성화되면, r이 감소합니다.
혼합이 상한선으로 포화되면, 명령된 추력이 감소되어 모터가 100 % 이상의 추력을 전달하지 않도록 합니다. 이 동작은 Airmode 로직과 유사하며 Airmode 활성화 여부에 관계없이 적용됩니다.
Once your vehicle flies well you can enable Airmode via the MC_AIRMODE parameter.