Visual Inertial Odometry (VIO)
Visual Inertial Odometry (VIO) is a computer vision technique used for estimating the 3D pose (local position and orientation) and velocity of a moving vehicle relative to a local starting position. GPS가 없거나 신뢰할 수없는 상황 (예 : 실내 또는 다리 아래에서 비행시)에서 기체 내비게이션용으로 사용됩니다.
VIO uses Visual Odometry to estimate vehicle pose from camera images, combined with inertial measurements from the vehicle IMU (to correct for errors associated with rapid vehicle movement resulting in poor image capture).
This topic gives guidance on configuring PX4 and a companion computer for a VIO setup.
INFO
The suggested setup uses ROS for routing VIO information to PX4. However, PX4 itself does not care about the source of messages, provided they are provided via the appropriate MAVLink Interface.
Suggested Setup
A hardware and software setup for VIO is suggested in the sections below as an illustration of how to interface a VIO system with PX4. It makes use of an off-the-shelf tracking camera and a companion computer running ROS. ROS is used to read odometry information from the camera and supply it to PX4.
An example of a suitable tracking camera is the Intel® RealSense™ Tracking Camera T265.
카메라 장착
카메라를 보조 컴퓨터에 연결하고 프레임에 장착합니다.
- 가능하면 렌즈가 아래쪽을 향하도록 카메라를 장착하십시오 (기본값).
- Cameras are typically very sensitive to vibration; a soft mounting is recommended (e.g. using vibration isolation foam).
Companion Setup
To setup ROS and PX4:
On the companion computer, install and configure MAVROS.
Implement and run a ROS node to read data from the camera and publish the VIO odometry using MAVROS.
- See the VIO ROS node section below for details of the requirements for this node.
Follow the instructions below for tuning the PX4 EKF2 estimator.
비행 컨트롤러 연결을 확인하십시오.
TIP
You can use the QGroundControl MAVLink Inspector to verify that you're getting
ODOMETRYorVISION_POSITION_ESTIMATEmessages (or check forHEARTBEATmessages that have the component id 197 (MAV_COMP_ID_VISUAL_INERTIAL_ODOMETRY)).
:::
- Verify that VIO is set up correctly before your first flight!
ROS VIO node
In this suggested setup, a ROS node is required to
- interface with the chosen camera or sensor hardware,
- produce odometry messages containing the position estimate, which will be sent to PX4 using MAVROS, and
- publish messages to indicate the VIO system status.
The implementation of the ROS node will be specific to the camera used and will need to be developed to use the interface and drivers appropriate for the camera.
The odometry messages should be of the type nav_msgs/Odometry and published to the topic /mavros/odometry/out.
System status messages of the type mavros_msgs/CompanionProcessStatus should be published to the topic /mavros/companion_process/status. These should identify the component as MAV_COMP_ID_VISUAL_INERTIAL_ODOMETRY (197) and indicate the state of the system. Recommended status values are:
MAV_STATE_ACTIVEwhen the VIO system is functioning as expected,MAV_STATE_CRITICALwhen the VIO system is functioning, but with low confidence, andMAV_STATE_FLIGHT_TERMINATIONwhen the system has failed or the estimate confidence is unacceptably low.
PX4 Tuning
EKF2에서 외부 위치 정보를 사용하려면 다음 매개 변수를 설정하여야 합니다.
| 매개변수 | 외부 위치 추정 설정 |
|---|---|
| EKF2_EV_CTRL | Set horizontal position fusion, vertical vision fusion, velocity fusion, and yaw fusion according to your desired fusion model. |
| EKF2_HGT_REF | Set to Vision to use the vision as the reference sensor for altitude estimation. |
| EKF2_EV_DELAY | 측정 타임스탬프와 "실제" 캡처 시간 간의 차이로 설정합니다. For more information see below. |
| EKF2_EV_POS_X, EKF2_EV_POS_Y, EKF2_EV_POS_Z | Set the position of the vision sensor with respect to the vehicle's body frame. |
These can be set in QGroundControl > Vehicle Setup > Parameters > EKF2 (remember to reboot the flight controller in order for parameter changes to take effect).
For more detailed/additional information, see: Using PX4's Navigation Filter (EKF2) > External Vision System.
Tuning EKF2_EV_DELAY
EKF2_EV_DELAY is the Vision Position Estimator delay relative to IMU measurements. 즉, 비전 시스템 타임스탬프와 IMU 클록 (EKF2의 "기본 클록")에 의해 기록된 "실제" 캡처 시간 간의 차이입니다.
Technically this can be set to 0 if there is correct timestamping (not just arrival time) and timesync (e.g. NTP) between MoCap and (for example) ROS computers. In reality, this may need some empirical tuning because delays in the communication chain are very setup-specific. It is rare that a system is set up with an entirely synchronised chain!
IMU 속도와 EV 속도 사이의 오프셋을 확인하여 로그에서 대략적인 지연 추정치를 얻을 수 있습니다.
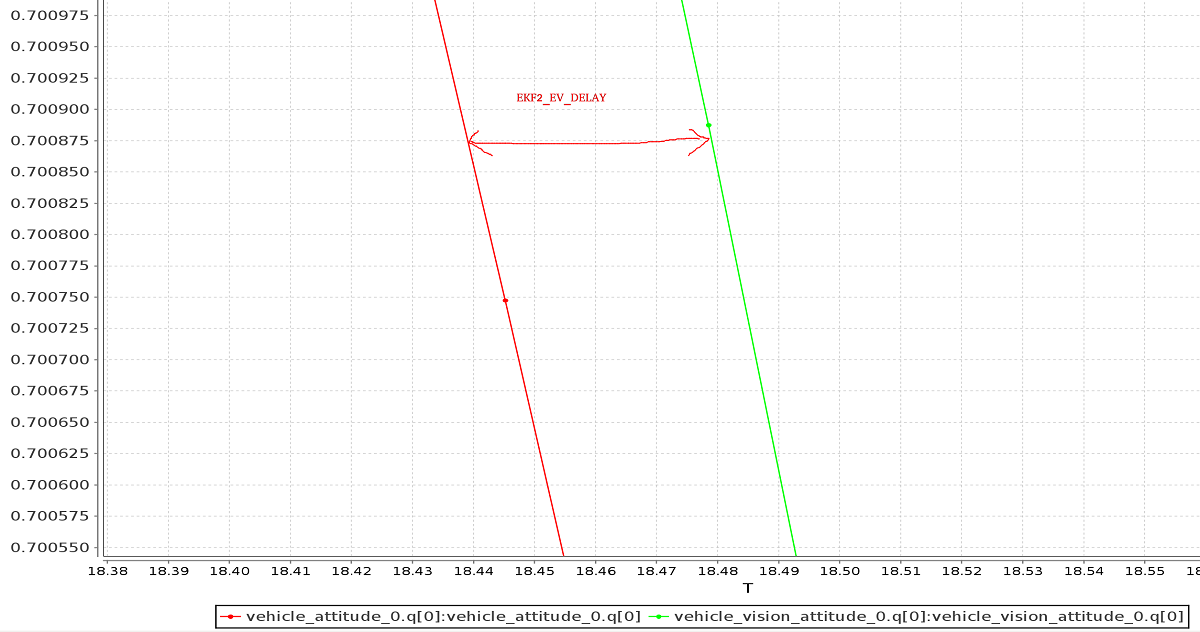
INFO
A plot of external data vs. onboard estimate (as above) can be generated using FlightPlot or similar flight analysis tools.
이 값은 동적 기동 중에 가장 낮은 EKF 혁신을 산출하는 값을 찾기 위하여, 매개변수를 변경하여 추가 튜닝할 수 있습니다.
Check/Verify VIO Estimate
INFO
The MAV_ODOM_LP parameter mentioned below was removed in PX4 v1.14. This section needs to be updated.
Perform the following checks to verify that VIO is working properly before your first flight:
- Set the PX4 parameter
MAV_ODOM_LPto1. PX4 will then stream back the received external pose as MAVLink ODOMETRY messages. You can check these MAVLink messages with the QGroundControl MAVLink Inspector - Yaw the vehicle until the quaternion of the
ODOMETRYmessage is very close to a unit quaternion (w=1, x=y=z=0).- At this point, the body frame is aligned with the reference frame of the external pose system.
- 기체를 구르거나 피칭하지 않고 단위 쿼터니언에 가까운 쿼터니언을 얻을 수 없다면, 여전히 프레임에 피치 또는 롤 오프셋이 있을 수 있습니다. 이 경우에는 더 이상 진행하지 말고, 좌표 프레임을 다시 확인하십시오.
- Once aligned, you can pick the vehicle up from the ground and you should see the position's z coordinate decrease. Moving the vehicle in the forward direction should increase the position's x coordinate. Moving the vehicle to the right should increase the y coordinate.
- Check that linear velocities in the message are expressed in the FRD body frame reference frame.
- Set the PX4 parameter
MAV_ODOM_LPback to 0. PX4 will stop streaming theODOMETRYmessage back.
이러한 단계가 유지되면, 첫 번째 비행을 시도할 수 있습니다.
Put the vehicle on the ground and start streaming
ODOMETRYfeedback (as above). 스로틀 스틱을 내리고 모터를 작동시키십시오.이때 왼쪽 스틱을 가장 낮은 위치에 놓고, 위치 제어로 전환합니다. 초록불이 켜져야 합니다. 녹색 표시등은 위치 피드백을 사용할 수 있고, 위치 제어가 활성화되었음을 알려줍니다.
기체가 고도를 유지하도록 스로틀 스틱을 중간(데드 존)에 놓습니다. 스틱을 올리면 기준 고도가 증가하고 값을 낮추면 감소합니다. Similarly, the other stick will change the position over the ground.
Increase the value of the throttle stick and the vehicle will take off. Move it back to the middle immediately afterwards.
기체가 제자리를 유지하는 지 확인하십시오.
문제 해결
First, make sure MAVROS is able to connect successfully to the flight controller.
제대로 연결되는 경우 일반적인 문제 해결 방법은 다음과 같습니다.
Problem: I get drift / flyaways when the drone flies, but not when I carry it around with the props off.
- If using the T265 try soft-mounting it (this camera is very sensitive to high-frequency vibrations).
Problem: I get toilet-bowling when VIO is enabled.
- 카메라의 방향이 시작 파일의 변환과 일치하는 지 확인합니다. Use the QGroundControl MAVLink Inspector to verify that the velocities in the
ODOMETRYmessage coming from MAVROS are aligned to the FRD coordinate system.
- 카메라의 방향이 시작 파일의 변환과 일치하는 지 확인합니다. Use the QGroundControl MAVLink Inspector to verify that the velocities in the
Problem: I want to use vision position to do loop closing, and also want to run GPS.
- 이문제는 EKF를 혼란스럽게 할 것이기 때문에 정말 어렵습니다. 테스트에서 비전 속도를 사용하는 것이 더 안정적입니다 (이 설정을 신뢰할 수있는 방법을 찾으면 알려주십시오).
개발자 정보
Developers who are interested in extending this implementation (or writing a different one, which might not depend on ROS) should see Using Vision or Motion Capture Systems for Position Estimation.
이 항목에서는 LPE Estimator (사용되지 않음)와 함께 사용할 VIO를 구성하는 방법도 설명합니다.